结构
insert
list 没有find,算法库有
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
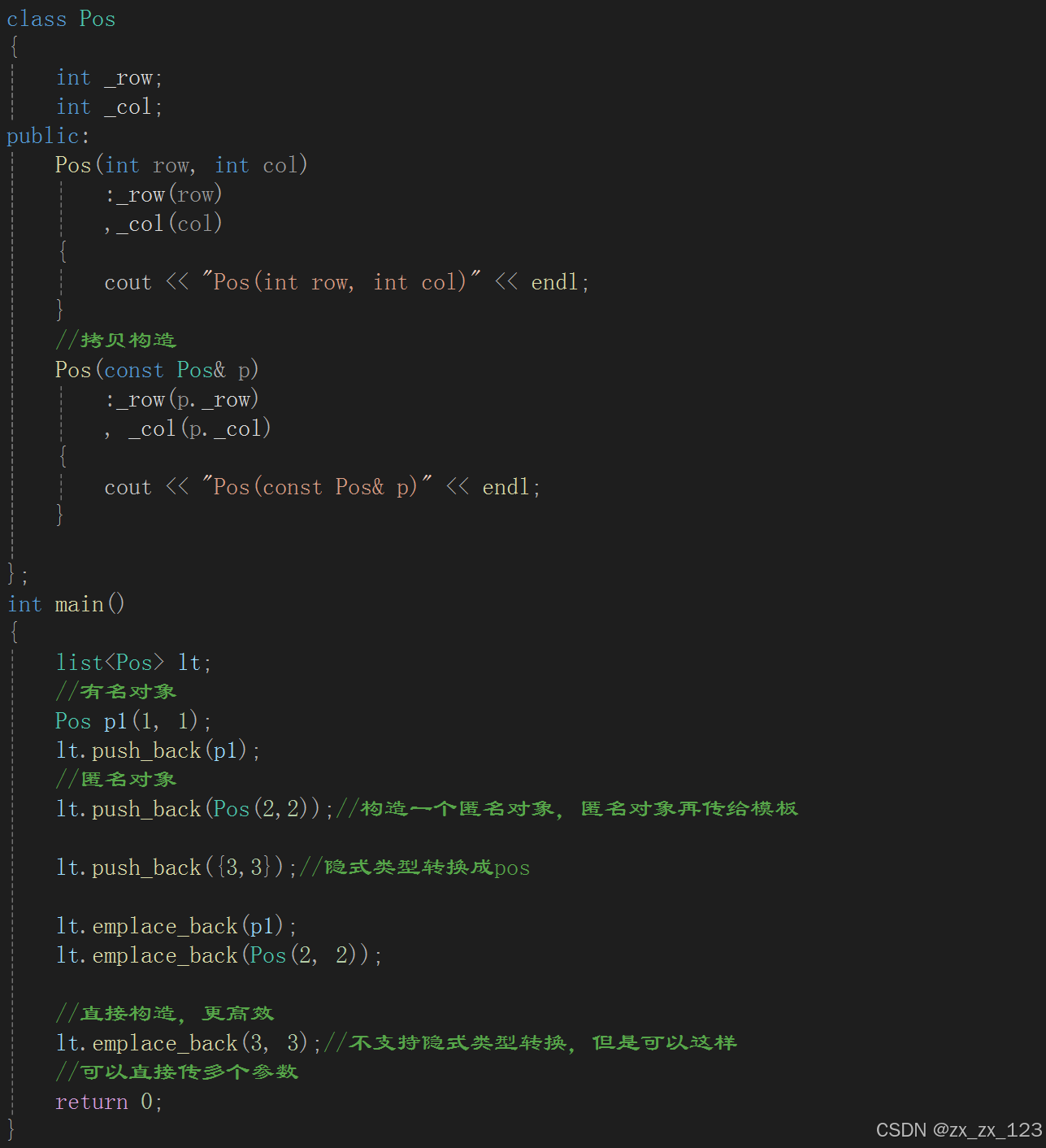
class Pos
{
int _row;
int _col;
public:
Pos(int row, int col)
:_row(row)
,_col(col)
{
cout << "Pos(int row, int col)" << endl;
}
//拷贝构造
Pos(const Pos& p)
:_row(p._row)
, _col(p._col)
{
cout << "Pos(const Pos& p)" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
list<int>lt1 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
for (auto e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
int x;
cin >> x;
auto it = find(lt1.begin(), lt1.end(),x);//在一段区间里进行查找
if (it != lt1.end())
{
lt1.erase(it);
}
for (auto e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}reverse 逆置
merge 归并(有序后)
unique 去重(有序后)
remove 删除
remove_if 带条件地删
splice 把一个链表的值转移给另一个链表
可以用来调整链表里面结点的顺序
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<list>
using namespace std;
class Pos
{
int _row;
int _col;
public:
Pos(int row, int col)
:_row(row)
,_col(col)
{
cout << "Pos(int row, int col)" << endl;
}
//拷贝构造
Pos(const Pos& p)
:_row(p._row)
, _col(p._col)
{
cout << "Pos(const Pos& p)" << endl;
}
};
int main()
{
list<int>lt1 = { 1,2,3,4,5 };
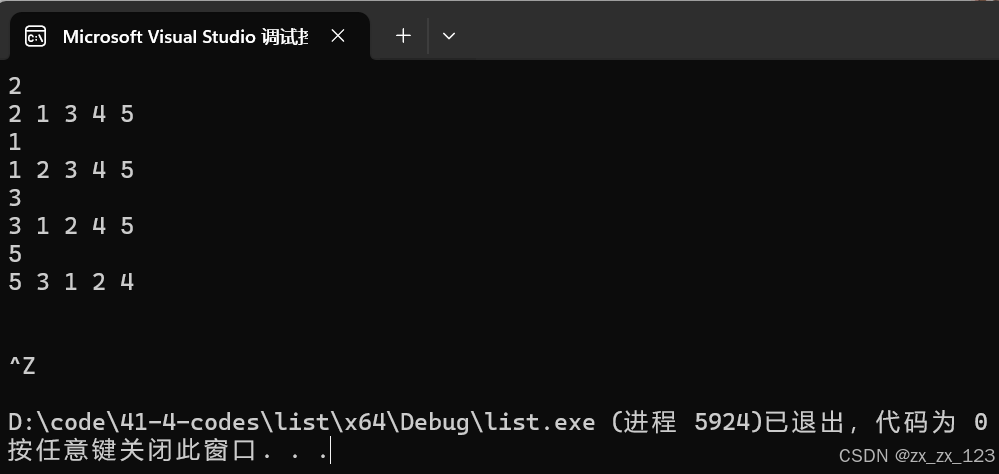
//LRU//最近最少用
int x;//找到了这个值代表这个值最近访问了,转移到头部
while (cin >> x)
{
auto pos = find(lt1.begin(), lt1.end(), x);//在一段区间里进行查找
if (pos != lt1.end())
{
lt1.splice(lt1.begin(), lt1, pos);
}
for (auto e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
return 0;
}
退出ctrl+z+回车/ctrl+c
https://legacy.cplusplus.com/reference/
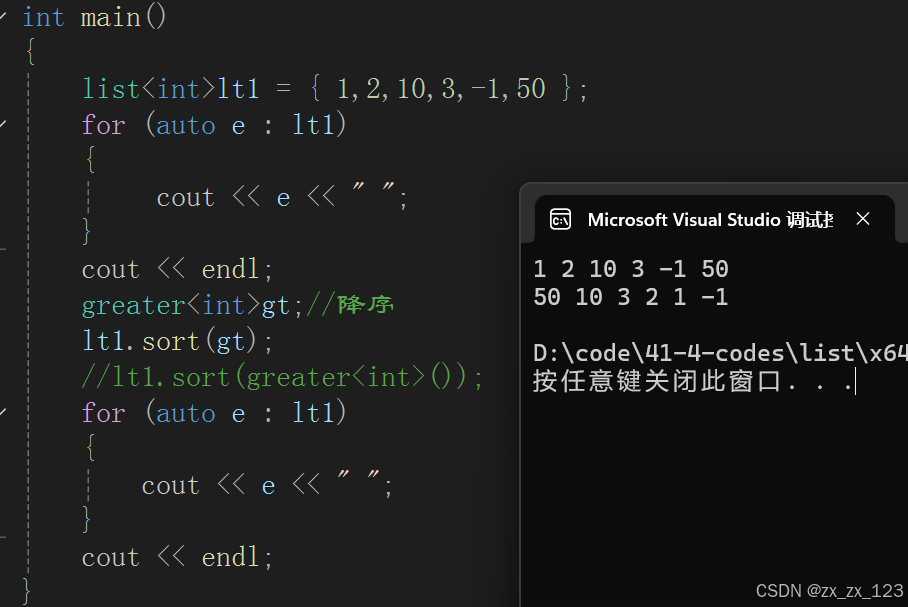
排序
(前面那部分都是一样的)
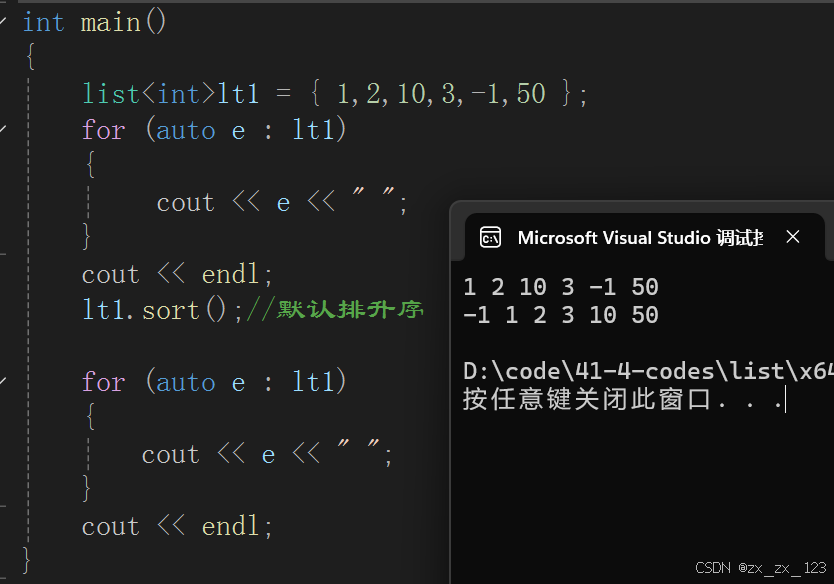
int main()
{
list<int>lt1 = { 1,2,10,3,-1,50 };
for (auto e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
greater<int>gt;//降序
lt1.sort(gt);
//lt1.sort(greater<int>());
for (auto e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
vector<int> v1 = { 1,2,10,3,-1,50 };
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
sort(v1.begin(), v1.end());
for (auto e : v1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
return 0;
}单向迭代器 ++ forward_list/unordered_xxx
双向迭代器 ++/-- list
随机迭代器 ++/--/+/- string/vector
list的迭代器失效
迭代器失效即迭代器所指向的节点无效,即该节点被删除了,因为list的底层结构为带头结点的双向循环链表,因此在list中进行插入时是不会导致list的迭代器失效的,只有在删除时才会失效,并且失效的只是指向被删除节点的迭代器,其他迭代器不会受到影响
list的模拟实现
用类去封装一个结点的指针
(头文件中)
#pragma once
#include<assert.h>
namespace DD
{
// 全部都是公有,一般用struc
template<class T>
struct list_node
{
T_data;
list_node<T>* _next;
list_node<T>* _prev;
list_node(const T& x=T())//匿名对象给缺省值
:_data(x)
,_next(nullptr)
,_prev(nullptr)
{}
};
template<class T>
struct list_iterator//用类去封装节点的指针,然后重载运算符
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
typedef list_node<T> Self;
Node* _node;
list_iterator(Node* node)
:_node(node)
{}
T& operator*()//出了作用域这个对象还在
{
return _node->_data;
}
T* operator->()
{
return &_node->_data;
}
//重载
Self& operator++()
{
_node = _node->_next;
return *this;//返回自己
}
Self operator++(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_next;
return tmp;
}
Self& operator--()
{
_node = _node->_prev;
return *this;//返回自己
}
Self operator--(int)
{
Self tmp(*this);
_node = _node->_prev;
return tmp;
}
bool operator!=(const Self& s)
{
return _node != s._node;
}
};
template<class T>
class list
{
typedef list_node<T> Node;
public:
typedef list_node<T> iterator;//对外所有容器的迭代器不管他叫什么都叫iterator
//提供开始位置的迭代器
iterator begin()
{
return iterator(_head->next);
}
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);//end就是head
}
//始终保持带头双向循环的状态,哪怕是空的
void empty_init()
{
_head = new Node;
_head->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = _head;
}
list()
{
empty_init();
}
void push_back(constT& x)
{
Node* new_node = new Node(x);
Node* tail = _head = _head->_prev;
tail->_next = new_node;
new_node->_prev = tail;
new_node->_next = _head;
_head->_prev = new_node;
}
list()
{
empty_init();
}
private:
Node* _hed;
};
}#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS 1
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<list>
#include<vector>
using namespace std;
class Pos
{
int _row;
int _col;
public:
Pos(int row, int col)
:_row(row)
,_col(col)
{
cout << "Pos(int row, int col)" << endl;
}
//拷贝构造
Pos(const Pos& p)
:_row(p._row)
, _col(p._col)
{
cout << "Pos(const Pos& p)" << endl;
}
};
void test_op1()
{
srand(time(0));
const int N = 1000000;
list<int> lt1;
list<int> lt2;
vector<int> v;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
auto e = rand() + i;
lt1.push_back(e);
v.push_back(e);
}
int begin1 = clock();
// 排序
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
int end1 = clock();
int begin2 = clock();
lt1.sort();
int end2 = clock();
printf("vector sort:%d\n", end1 - begin1);
printf("list sort:%d\n", end2 - begin2);
}
void test_op2()
{
srand(time(0));
const int N = 1000000;
list<int> lt1;
list<int> lt2;
for (int i = 0; i < N; ++i)
{
auto e = rand();
lt1.push_back(e);
lt2.push_back(e);
}
int begin1 = clock();
// 拷贝vector
vector<int> v(lt2.begin(), lt2.end());
// 排序
sort(v.begin(), v.end());
// 拷贝回lt2
lt2.assign(v.begin(), v.end());
int end1 = clock();
int begin2 = clock();
lt1.sort();
int end2 = clock();
printf("list copy vector sort copy list sort:%d\n", end1 - begin1);
printf("list sort:%d\n", end2 - begin2);
}
#include"List.h"
int main()
{
DD::list<int>lt1;//构造空的l1
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(1);
lt1.push_back(1);
DD::list<int>::iterator it1 = lt1.begin();
while (it1 != lt1.end())
{
*it1 = 2;
cout << *it1 << " ";
++it1;
}
cout << endl;
for (auto e : lt1)
{
cout << e << " ";
}
cout << endl;
DD::list<Pos> lt2;
Pos p1(1, 1);
lt2.push_back(p1);
lt2.push_back(Pos(2, 2));
lt2.push_back({ 3,3 });
DD::list<Pos>::iterator it2 = lt2.begin();
//结构体类型访问用->
while (it2 != lt2.end())
{
//cout << (*it2)._row << ":" << (*it2)._col << endl;
// 为了可读性,特殊处理,省略了一个->
cout << it2->_row << ":" << it2->_col << endl;
cout << it2.operator->()->_row << ":" << it2.operator->()->_col << endl;//显示
++it2;
}
cout << endl;
}const迭代器(不用写析构函数)的实现
insert
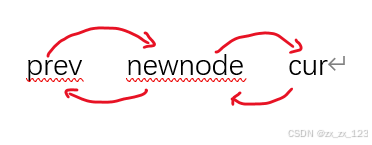
iterator insert(iterator pos, const T& val)//在pos之前插入一个值,可以在任意位置插入
{
//最终还是要拿到这个结点的指针
//找到他的前一个,也不用判断是否为空
Node* cur = pos._node;
Node* newnode = new Node(val);//创建一个新的
Node* prev = cur->_prev;
prev->_next = newnode;
newnode->_prev = prev;
//插入
newnode->next = cur;
cur->_prev = newnode;
return iterator(newnode);//返回一个迭代器,指向新插入的元素
}erase
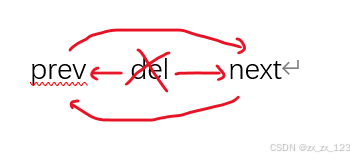
iterator erase(iterator pos)//删除pos位置
{
assert(pos != end())//所有位置都可以删除,不能删哨兵位头节点
//end() 哨兵位头节点构造的迭代器
/* iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);
}*/
//找到他的前一个和后一个,让他的前一个和后一个连接起来
Node* del = pos._node;
Node* prev = del->_prev;
Node* next = del->_next;
prev->_next = next;
next->_prev = prev;
delete del;
return iterator(next);//返回删除位置的下一个
}头插
在end()前面插入
iterator end()
{
return iterator(_head);
}
void push_front()
{
insert(begin(), x);
}头删 删begin()
void pop _front()
{
erase(begin());
}尾删
void pop_back()
{
rease(--end());
}全部走复用
swap
交换头节点
void swap(list<T>& tmp)
{
std::swap(_head, tmp._head);
}clear 所有的值都要删掉但哨兵位的头节点不动
~析构 所有的值都要删掉,哨兵位也得拿走
拷贝构造
//lt2(lt1)
list(const list<T>& lt)
{
empty_init();//lt2 先把哨兵位的头结点开出来再初始化一下
//范围for遍历lt1 ,取里面的数据,范围for自己转到迭代器
//再push_back,lt2 push_back会建立结点
for (auto& e : lt)//这里的&,取它里面的数据,*lt赋值给e不加&就是一种拷贝
{
push_back(e);
}
}