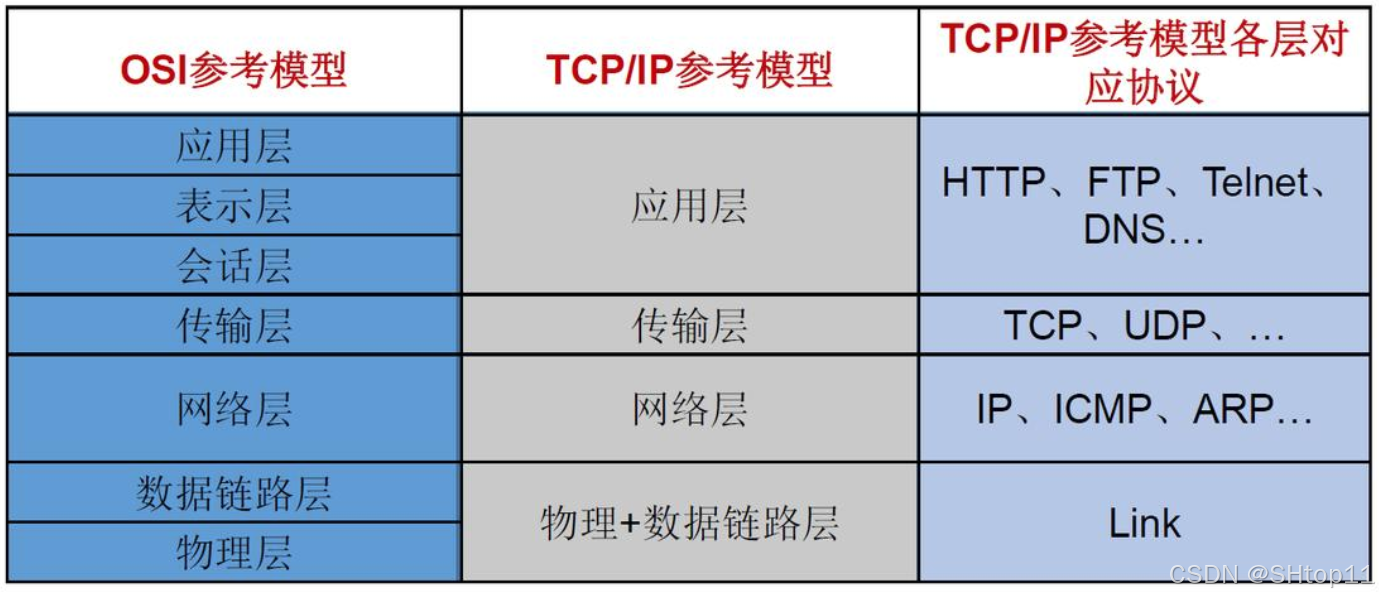
网络通信协议
java.net 包中提供了两种常见的网络协议的支持:
- UDP:用户数据报协议(User Datagram Protocol)
- TCP:传输控制协议(Transmission Control Protocol)
TCP协议与UDP协议
TCP协议
- TCP协议进行通信的两个应用进程:客户端、服务端
- 使用TCP协议前,须先建立TCP连接,形成基于字节流的传输数据通道
- 传输前,采用“三次握手”方式,点对点通信,是可靠的
- TCP协议使用重发机制,当一个通信实体发送一个消息给另一个通信实体后,需要收到另一个通信实体确认信息,如果没有收到另一个通信实体确认信息,则会再次重复刚才发送的消息
- 在连接中可进行大数据量的传输
传输完毕,需释放已建立的连接,效率低
UDP协议
- UDP协议进行通信的两个应用进程:发送端、接收端
- 将数据、源、目的封装成数据包(传输的基本单位),不需要建立连接
- 发送不管对方是否准备好,接收方收到也不确认,不能保证数据的完整性,故是不可靠的
- 每个数据报的大小限制在64K内
- 发送数据结束时无需释放资源,开销小,通信效率高
- 适用场景:音频、视频和普通数据的传输。例如视频会议
生活案例
TCP生活案例:打电话
UDP生活案例:发送短信、发电报
区别
- TCP:可靠的连接(发送数据前,需要三次握手、四次挥手),进行大数据量的传输,效率低。
- UDP:不可靠的连接(发送前,不需要确认对方是否在)、使用数据报传输(限制在64kb以内)、效率高。
TCP协议
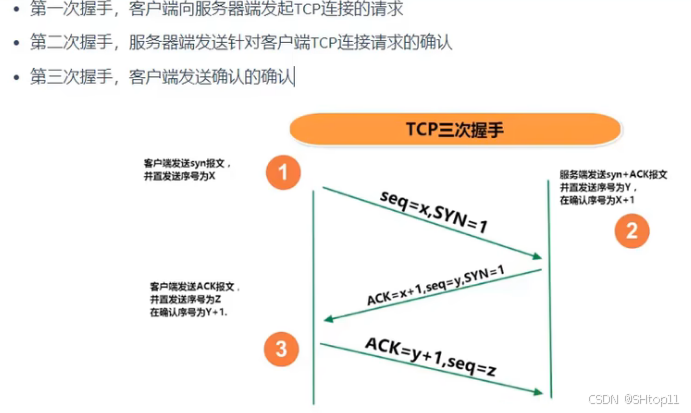
三次握手
TCP协议中,在发送数据的准备阶段,客户端与服务器之间的三次交互,以保证连接的可靠。
完成三次握手,连接建立后,客户端和服务器就可以开始进行数据传输了。由于这种面向连接的特性,TCP协议可以保证传输数据的安全,所以应用十分广泛,例如下载文件、浏览网页等。
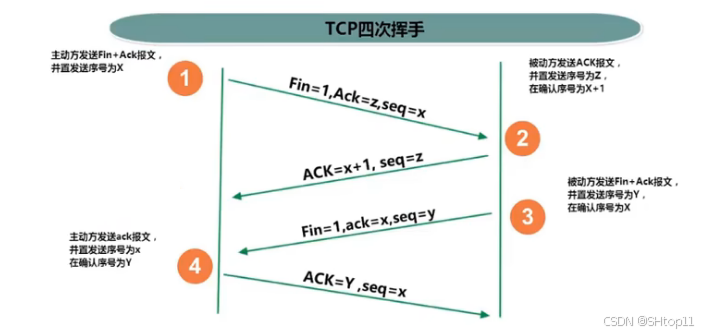
四次挥手
TCP协议中,在发送数据结束后,释放连接时需要经过四次挥手。
- 第一次挥手:客户端向服务器端提出结束连接,
让服务器做最后的准备工作。此时,客户端处于半关闭状态,即表示不再向服务器发送数据了,但是还可以接受数据。 - 第二次挥手:服务器接收到客户端释放连接的请求后,
会将最后的数据发给客户端。并告知上层的应用进程不再接收数据。 - 第三次挥手:服务器发送完数据后,会给客户端
发送一个释放连接的报文。那么客户端接收后就知道可以正式释放连接了。 - 第四次挥手:客户端接收到服务器最后的释放连接报文后,要
回复一个彻底断开的报文。这样服务器收到后才会彻底释放连接。这里客户端,发送完最后的报文后,会等待2MSL,因为有可能服务器没有收到最后的报文,那么服务器迟迟没收到,就会再次给客户端发送释放连接的报文,此时客户端在等待时间范围内接收到,会重新发送最后的报文,并重新计时。如果等待2MSL后,没有收到,那么彻底断开。
网络编程API
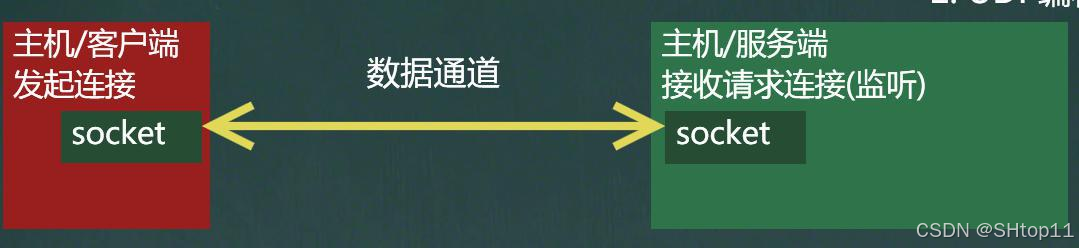
Socket类
基本介绍
示意图:
理解客户端、服务端
-
客户端:
- 自定义
- 浏览器(browser — server)
-
服务端:
- 自定义
- Tomcat服务器
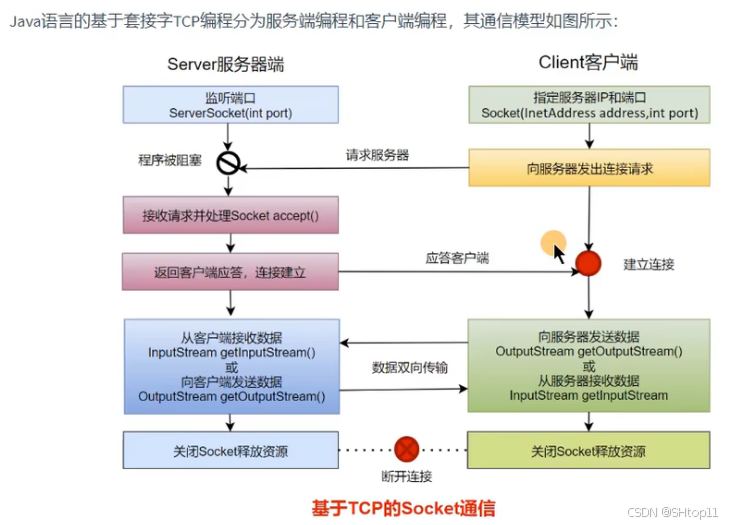
TCP网络编程
通信模型
例题1
客户端发送内容给服务端,服务端将内容打印到控制台上。
public class TCPTest1 {
//客户端
@Test
public void client() {
Socket socket = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
// 1.创建一个Socket
InetAddress inetAddress = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1"); //声明ip地址
int port = 8989; //声明端口号
socket = new Socket(inetAddress,port);
// 2.发送数据
os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("你好,我是客户端,请多多关照".getBytes());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 3.关闭socket、流
try {
if (socket != null)
socket.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (os != null)
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//服务端
@Test
public void server() {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
Socket socket = null; //阻塞式方法
InputStream is = null;
try {
// 1.创建一个ServerSocket
int port = 8989;
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);
// 2.调用accept(),接收客户端的Socket
socket = serverSocket.accept();
System.out.println("服务器端已开启");
System.out.println("收到了来自于" + socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress() + "的连接");
// 3.接收数据
is = socket.getInputStream();
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream(); //内部维护了一个byte[]
int len;
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
// 错误的,可能会出现乱码
// String str = new String(buffer,0,len);
// System.out.println(str);
//正确的
baos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
System.out.println("\n数据接收完毕");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 4.关朗Socket、ServerSocket、流
try {
if (socket != null) {
socket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (serverSocket != null) {
serverSocket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
例题2
客户端发送文件给服务端,服务端将文件保存在本地。
public class TCPTest2 {
//客户端
@Test
public void client() {
// 1.创建Socket
// 指明对方(即为服务器)的ip地址和端口号
Socket socket = null;
FileInputStream fis = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
InetAddress inetAddress = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port = 9090;
socket = new Socket(inetAddress,port);
// 2.创建File的实例、FileInputstream的实例
File file = new File("huan.jpg");
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
// 3.通过Socket,获取输出流
os = socket.getOutputStream();
// 读写数据
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println("数据发送完毕");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 4.关闭Socket和相关的流
try {
if (os != null) {
os.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fis != null) {
fis.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (socket != null) {
socket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//服务端
@Test
public void server() {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
Socket socket = null;
InputStream is = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
try {
// 1.创建ServerSocket
int port = 9090;
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);
// 2.接收来自于客户端的socket:accept()
socket = serverSocket.accept();
// 3.通过Socket获取一个输入流
is = socket.getInputStream();
// 4.创建File类的实例、File0utputstream的实例
File file = new File("huan_copy.jpg");
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
// 5.读写过程
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer,0,len);
}
System.out.println("数据接收完毕");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 6.关闭相关的Socket和流
try {
if (fos != null) {
fos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (socket != null) {
socket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (serverSocket != null) {
serverSocket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
例题3
从客户端发送文件给服务端,服务端保存到本地。并返回“发送成功"给客户端。并关闭相应的连接。
public class TCPTest3 {
//客户端
@Test
public void client() {
// 1.创建Socket
// 指明对方(即为服务器)的ip地址和端口号
Socket socket = null;
FileInputStream fis = null;
OutputStream os = null;
ByteArrayOutputStream baos = null;
InputStream is = null;
try {
InetAddress inetAddress = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port = 9090;
socket = new Socket(inetAddress, port);
// 2.创建File的实例、FileInputstream的实例
File file = new File("huan.jpg");
fis = new FileInputStream(file);
// 3.通过Socket,获取输出流
os = socket.getOutputStream();
// 4.读写数据
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = fis.read(buffer)) != -1) {
os.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println("数据发送完毕");
// 5.客户端表明不再继续发送数据
socket.shutdownOutput();
// 6.接收来自于服务器端的数据
is = socket.getInputStream();
baos = new ByteArrayOutputStream();
byte[] buffer1 = new byte[5];
int len1;
while ((len1 = is.read(buffer1)) != -1) {
baos.write(buffer1, 0, len1);
}
System.out.println(baos.toString());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 7.关闭Socket和相关的流
try {
baos.close();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (os != null) {
os.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fis != null) {
fis.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (socket != null) {
socket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
//服务端
@Test
public void server() {
ServerSocket serverSocket = null;
Socket socket = null;
InputStream is = null;
FileOutputStream fos = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
// 1.创建ServerSocket
int port = 9090;
serverSocket = new ServerSocket(port);
// 2.接收来自于客户端的socket:accept()
socket = serverSocket.accept();
// 3.通过Socket获取一个输入流
is = socket.getInputStream();
// 4.创建File类的实例、File0utputstream的实例
File file = new File("huan_copy2.jpg");
fos = new FileOutputStream(file);
// 5.读写过程
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1) {
fos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
// 6.服务端发送数据给客户端
os = socket.getOutputStream();
os.write("你的图片很漂亮,我接收到了".getBytes());
System.out.println("数据接收完毕");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 7.关闭相关的Socket和流
try {
os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (fos != null) {
fos.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (socket != null) {
socket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (serverSocket != null) {
serverSocket.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if (is != null) {
is.close();
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
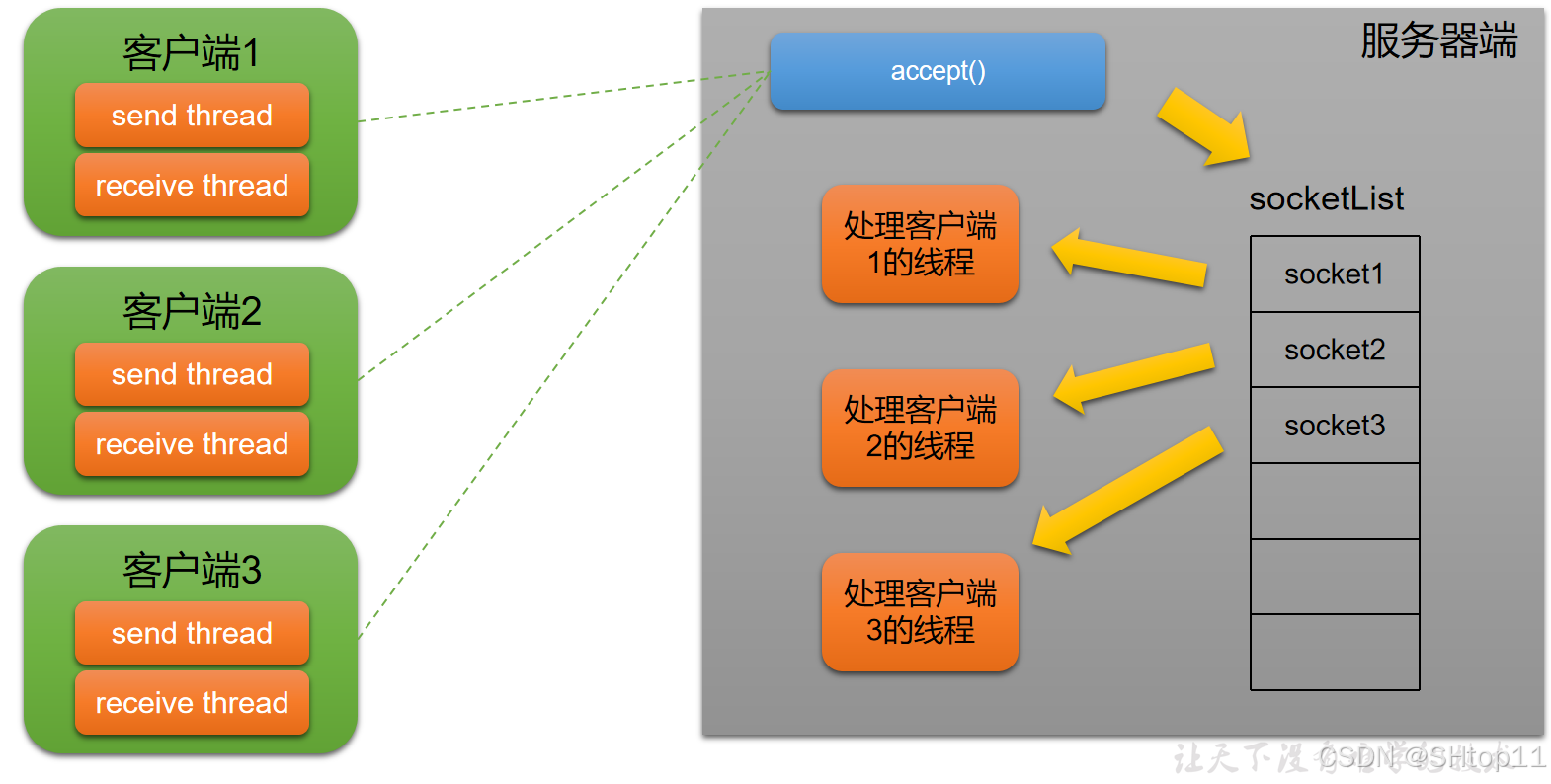
【案例】聊天室
聊天室模型
服务器端
public class ChatSeverTest {
//这个集合用来存储所有在线的客户端
static ArrayList<Socket> online = new ArrayList<Socket>();
public static void main(String[] args) throws IOException {
//1、启动服务器,绑定端口号
ServerSocket server = new ServerSocket(8989);
//2、接收n多的客户端同时连接
while (true) {
Socket accept = server.accept();
online.add(accept);//把新连接的客户端添加到online列表中
MessageHandler mh = new MessageHandler(accept);
mh.start();
}
}
static class MessageHandler extends Thread {
private Socket socket;
private String ip;
public MessageHandler(Socket socket) {
super();
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
ip = socket.getInetAddress().getHostAddress();
//插入:给其他客户端转发“我上线了”
sendToOther(ip+"上线了");
//(1)接收该客户端的发送的消息
InputStream input = socket.getInputStream();
InputStreamReader reader = new InputStreamReader(input);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(reader);
String str;
while ((str = br.readLine()) != null) {
//(2)给其他在线客户端转发
sendToOther(ip + ":" + str);
}
sendToOther(ip + "下线了");
} catch (IOException e) {
try {
sendToOther(ip + "掉线了");
} catch (Exception e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
} finally {
//从在线人员中移除我
online.remove(socket);
}
}
//封装一个方法:给其他客户端转发xxx消息
public void sendToOther(String message) throws IOException {
//遍历所有的在线客户端,一一转发
for (Socket on : online) {
OutputStream every = on.getOutputStream();
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(every);
ps.println(message);
}
}
}
}
客户端
public class ChatClientTest {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
//1、连接服务器
Socket socket = new Socket("127.0.0.1", 8989);
//2、开启两个线程
//(1)一个线程负责看别人聊,即接收服务器转发的消息
Receive receive = new Receive(socket);
receive.start();
//(2)一个线程负责发送自己的话
Send send = new Send(socket);
send.start();
send.join();//等我发送线程结束了,才结束整个程序
socket.close();
}
}
class Send extends Thread{
private Socket socket;
public Send(Socket socket) {
super();
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
OutputStream outputStream = socket.getOutputStream();
//按行打印
PrintStream ps = new PrintStream(outputStream);
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
//从键盘不断的输入自己的话,给服务器发送,由服务器给其他人转发
while (true) {
System.out.println("自己的话:");
String str = input.nextLine();
if ("bye".equals(str)) {
break;
}
ps.println(str);
}
input.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
class Receive extends Thread{
private Socket socket;
public Receive(Socket socket) {
super();
this.socket = socket;
}
@Override
public void run() {
try {
InputStream inputStream = socket.getInputStream();
Scanner input = new Scanner(inputStream);
while (input.hasNextLine()) {
String line = input.nextLine();
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
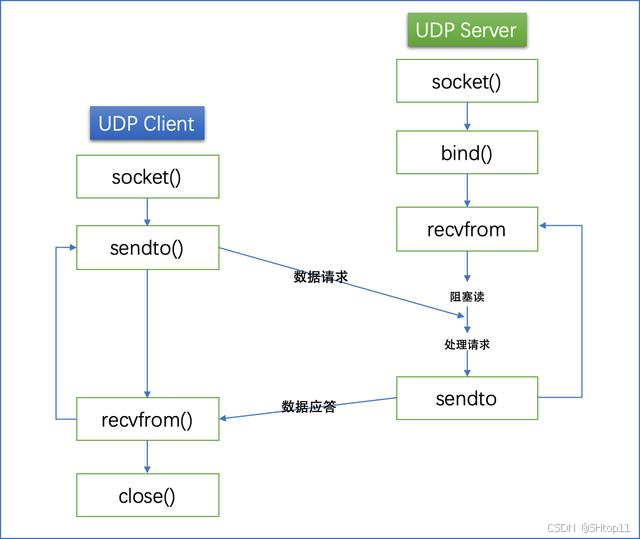
UDP网络编程
通信模型
示例
public class UDPTest {
//发送端
@Test
public void sender() throws Exception {
//1.创建DatagramSocket的实例
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket();
//2、将数据、目的地的ip,目的地的端口号部封装在DatagramPacket数据报中
InetAddress inetAddress = InetAddress.getByName("127.0.0.1");
int port = 9090;
byte[] bytes = "我是发送端".getBytes("utf-8");
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(bytes, 0, bytes.length, inetAddress, port);
//发送数据
ds.send(packet);
ds.close();
}
//接收端
@Test
public void receiver() throws IOException {
//1.创建DatagramSocket的实例
int port = 9090;
DatagramSocket ds = new DatagramSocket(port);
//2. 创建数据报的对象,用于接收发送端发送过来的数据
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024 * 64];
DatagramPacket packet = new DatagramPacket(buffer, 0, buffer.length);
//3.接收数据
ds.receive(packet);
//4.获取数据,并打印到控制台上
String str = new String(packet.getData(), 0, packet.getLength());
System.out.println(str);
ds.close();
}
}