1、基础
1.1、JavaScript 介绍
-
JavaScript 是一种客户端脚本语言。运行在客户端浏览器中,每一个浏览器都具备解析 JavaScript 的引擎。
-
脚本语言:不需要编译,就可以被浏览器直接解析执行了。
-
核心功能就是增强用户和 HTML 页面的交互过程,让页面有一些动态效果。以此来增强用户的体验!
1.2、快速入门
- 实现步骤
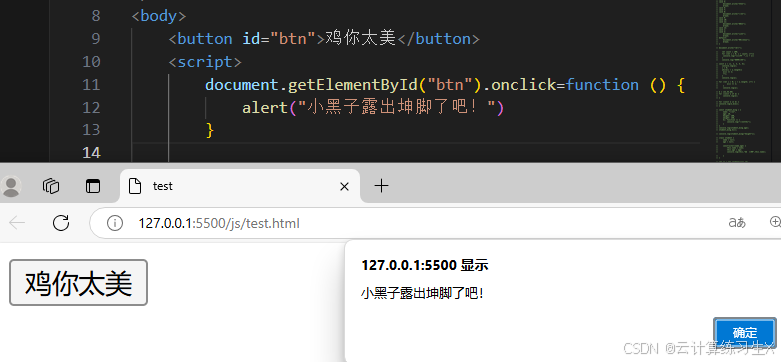
- 创建一个 HTML。
- 在标签下面编写一个
<script>标签。 - 在
<script>标签中编写代码。 - 通过浏览器查看
- 具体实现
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>test</title>
</head>
<body>
<button id="btn">鸡你太美</button>
</body>
</html>
引入js的方式一:内部方式
内部方式:<script></script>
<script>
document.getElementById("btn").onclick=function () {
alert("小黑子露出坤脚了吧!");
}
</script>
引入js的方式一:外部方式
-
创建js文件
document.getElementById("btn").onclick=function () { alert("小黑子露出坤脚了吧!"); } -
在 html 中引用外部 js 文件
<script src="js/my.js"></script>
1.3、开发环境搭建
2、JavaScript基本语法
2.1、注释
-
单行注释
// 注释的内容 -
多行注释
/* 注释的内容 */
2.2、输入输出语句
- 输入框 prompt(“提示内容”);
- 弹出警告框 alert(“提示内容”);
- 控制台输出 console.log(“显示内容”);
- 页面内容输出 document.write(“显示内容”);
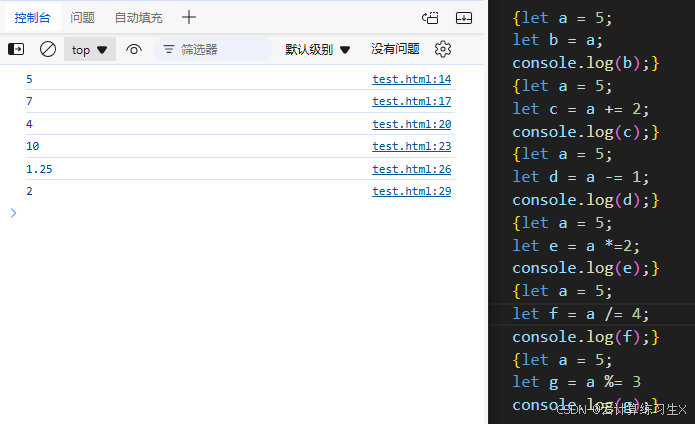
2.3、变量和常量
JavaScript 属于弱类型的语言,定义变量时不区分具体的数据类型。
-
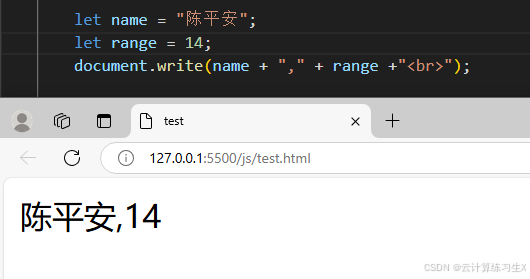
定义局部变量 let 变量名 = 值;
//1.定义局部变量 let name = "陈平安"; let range = 18; document.write(name + "," + range +"<br>");
-
定义全局变量 变量名 = 值;
//2.定义全局变量 { let l1 = "aa"; } l2 = "bb"; //l1局部变量;l2全局变量 document.write(l2 + "<br>"); -
定义常量 const 常量名 = 值;
//3.定义常量 const PI = 3.1415926; document.write(PI);
2.4、原始数据类型和typeof方法
2.4.1、原始数据类型
2.4.2、typeof
typeof 用于判断变量的数据类型
let age = 18;
document.write(typeof(age)); // number
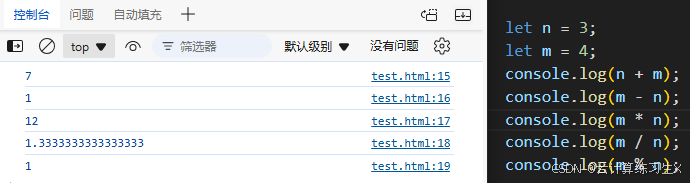
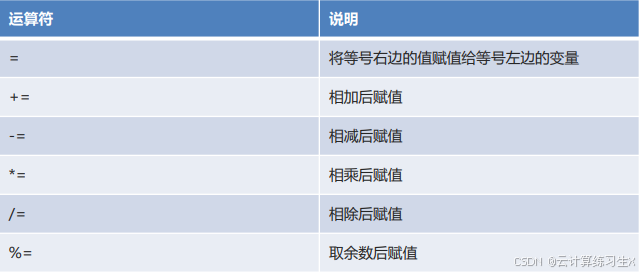
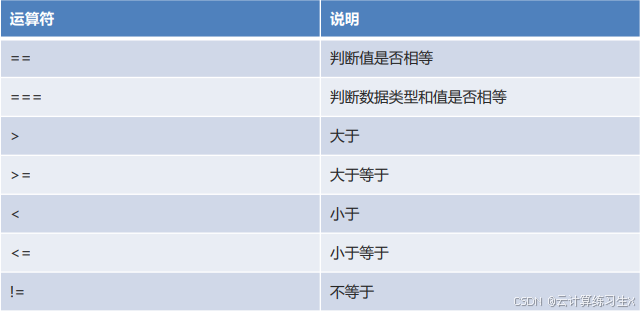
2.5、运算符
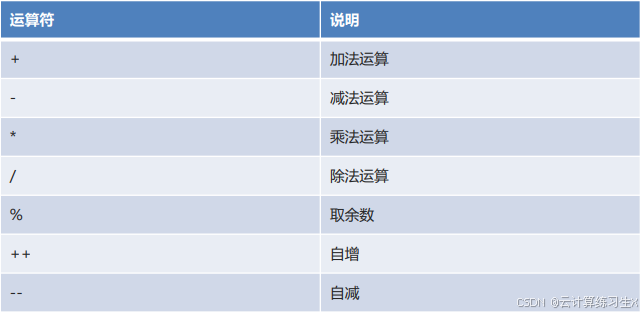
- 算数运算符
- 赋值运算符
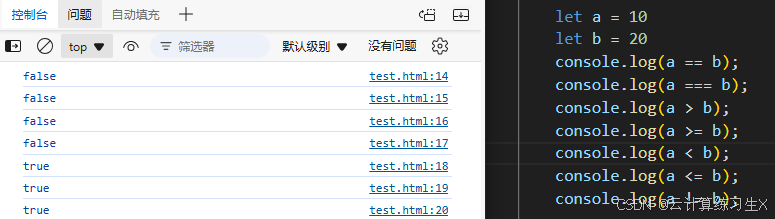
- 比较运算符
注:值皆为布尔值
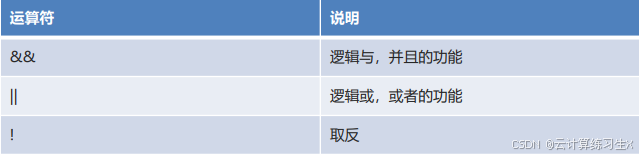
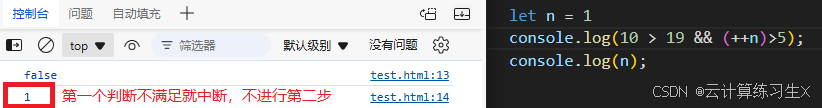
- 逻辑运算符
注:值皆为布尔值
-
三元运算符
-
三元运算符格式
(比较表达式) ? 表达式1 : 表达式2;
-
执行流程
如果比较表达式为 true,则取表达式1
如果比较表达式为 false,则取表达式2
-
2.6、流程控制和循环语句
-
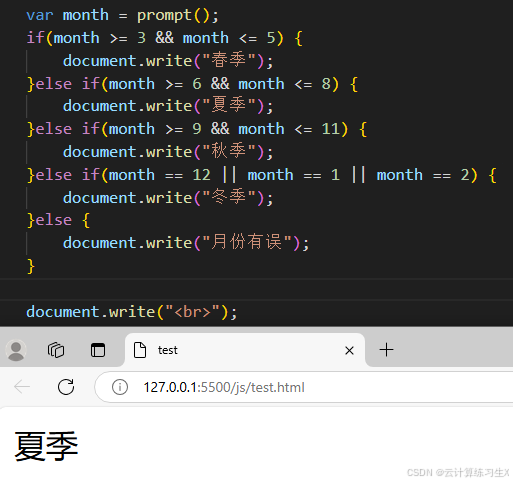
if 语句
//if语句 let month = 3; if(month >= 3 && month <= 5) { document.write("春季"); }else if(month >= 6 && month <= 8) { document.write("夏季"); }else if(month >= 9 && month <= 11) { document.write("秋季"); }else if(month == 12 || month == 1 || month == 2) { document.write("冬季"); }else { document.write("月份有误"); } document.write("<br>");
-
switch 语句
//switch语句 switch(month){ case 3: case 4: case 5: document.write("春季"); break; case 6: case 7: case 8: document.write("夏季"); break; case 9: case 10: case 11: document.write("秋季"); break; case 12: case 1: case 2: document.write("冬季"); break; default: document.write("月份有误"); break; } document.write("<br>");**for 循环**
-
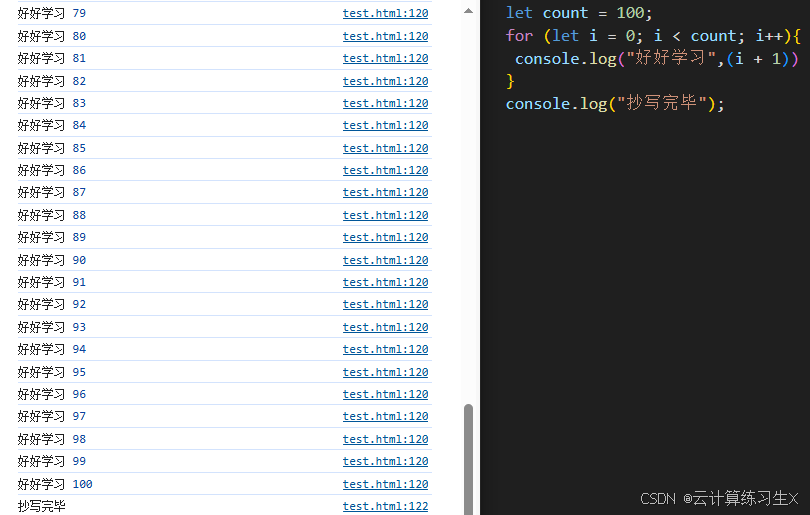
for 循环
//for循环 for(let i = 1; i <= 5; i++) { document.write(i + "<br>"); }例:
-
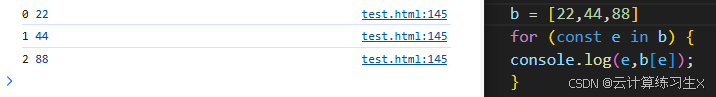
for in: 遍历对象
用于遍历对象的属性。
for...in 语句的语法如下:
for (variable in object) {
// 执行的代码
}
其中,variable 是一个变量,用于存储当前遍历到的属性名;object 是要遍历的对象。
for...in 语句的示例代码如下:
const person = {
name: "John",
age: 30,
city: "New York"
};
for (const key in person) {
console.log(key + ": " + person[key]);
}
当运行上述代码时,for...in 语句将遍历 person 对象的所有属性,并使用 console.log() 函数将每个属性名和属性值输出到控制台。
需要注意的是,for...in 语句会遍历对象的所有可枚举属性,包括原型链上的属性。如果您只想遍历对象自身的属性,可以使用 Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty() 方法进行检查。
此外,for...in 语句不要用于遍历数组。如果您需要遍历数组,可以使用 for 语句、for...of 语句或 Array.prototype.forEach() 方法。
例:
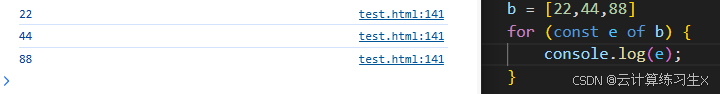
- for of: 遍历数组
// 遍历数组 memes: [12, 56, 78, 66]
for (const key in memes) {
console.log(typeof(key));
}
// output: string
for (const key of memes) {
console.log(typeof(key));
}
// output: number
例:
-
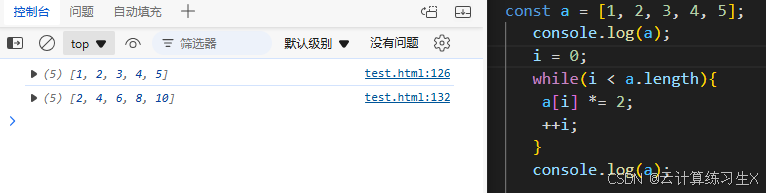
while 循环
//while循环 let n = 6; while(n <= 10) { document.write(n + "<br>"); n++; }例:
2.7、数组
-
数组的使用和 java 中的数组基本一致,但是在 JavaScript 中的数组更加灵活,数据类型和长度都没有限制。
-
定义格式
-
let 数组名 = [元素1,元素2,…]; -
let arr = [10, 20, 30];
-
-
索引范围
- 从 0 开始,最大到数组长度-1
-
数组长度
- 数组名.length
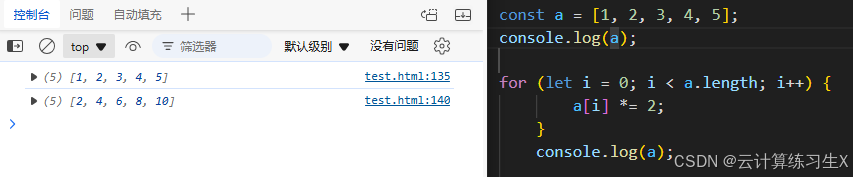
for(let i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
document.write(arr[i] + "<br>");
}
document.write("==============<br>");
例:
-
数组高级运算符…
-
Spread syntax (展开)
-
Math.max 方法不会作用于数组 arr,因为 Math.max 方法的参数只能是单个元素而不能是一个数组。扩展运算符可以从数组中提取出单个元素。
const arr = [4, 6, -1, 3, 10, 4];
const max = Math.max(...arr);
console.log(max);
// 10
例:
-
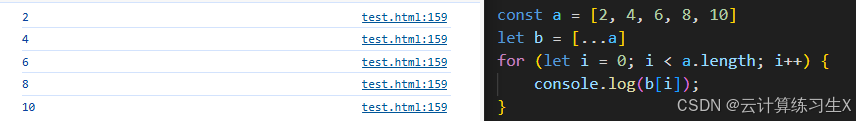
数组复制
//复制数组 let arr2 = [...arr]; //遍历数组 for(let i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++) { document.write(arr2[i] + "<br>"); } document.write("==============<br>");
例:
-
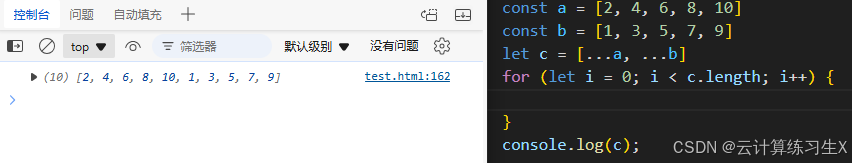
合并数组
//合并数组 let arr3 = [40,50,60]; let arr4 = [...arr2 , ...arr3]; //遍历数组 for(let i = 0; i < arr4.length; i++) { document.write(arr4[i] + "<br>"); } document.write("==============<br>");
例:
-
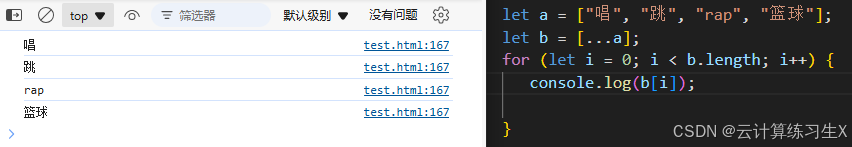
字符串转数组
//将字符串转成数组 let arr5 = [..."Cool"]; //遍历数组 for(let i = 0; i < arr5.length; i++) { document.write(arr5[i] + "<br>"); }
例:
2.8、函数
-
函数类似于 Java 中的方法,可以将一些代码进行抽取,达到复用的效果
-
定义格式
function 方法名(参数列表) { 方法体; return 返回值; } -
可变参数
function 方法名(...参数名) { 方法体; return 返回值; } -
匿名函数
function(参数列表) { 方法体; }
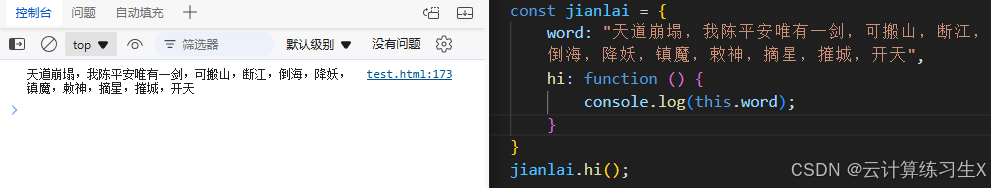
2.9 this
this 是 JavaScript 中的一个关键字,它表示当前执行上下文中的对象。this 的值取决于函数的调用方式,具体如下:
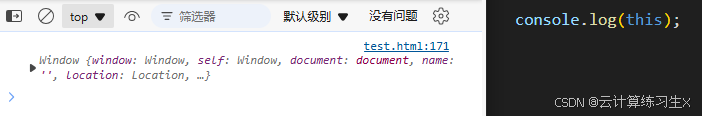
- 全局上下文中的
this:在全局上下文中,this指向全局对象。在浏览器环境中,全局对象是window;在 Node.js 环境中,全局对象是global。
// 全局上下文中的 this
console.log(this); // 输出:Window(浏览器环境)或 global(Node.js 环境)
例:
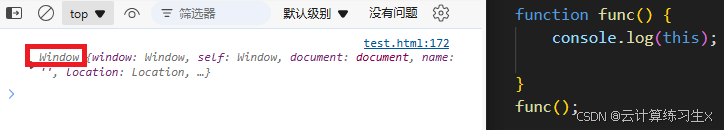
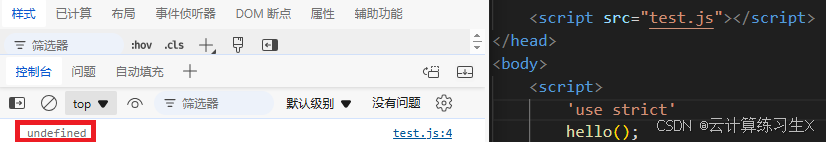
- 函数调用中的
this:在普通函数中,this指向全局对象。在严格模式下,this是undefined。
// 函数调用中的 this
function func() {
console.log(this);
}
func(); // 输出:Window(浏览器环境)或 global(Node.js 环境)
例:
- 对象方法调用中的
this:在对象方法中,this指向调用该方法的对象。
// 对象方法调用中的 this
const obj = {
func: function() {
console.log(this);
}
};
obj.func(); // 输出:obj
例:
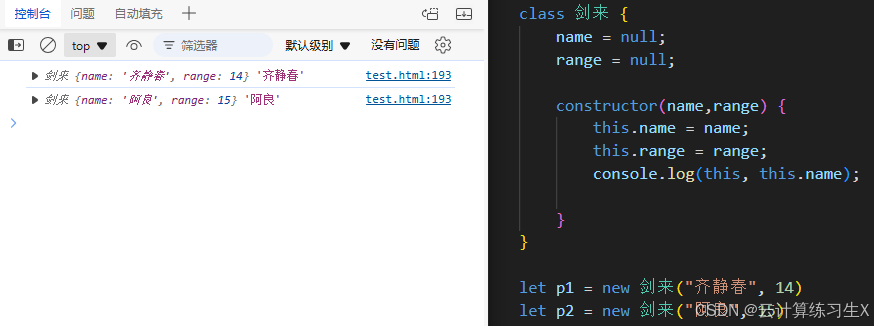
- 构造函数调用中的
this:在构造函数中,this指向新创建的对象。
// 构造函数调用中的 this
function Person(name) {
this.name = name;
}
const person = new Person("John");
console.log(person.name); // 输出:"John"
例:
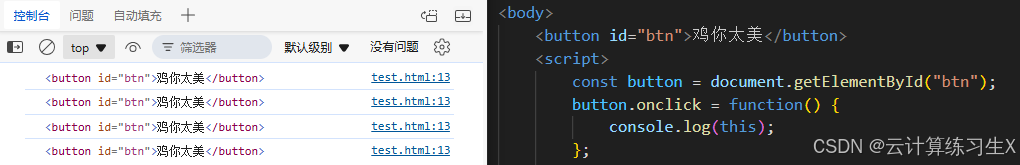
- 事件处理函数中的
this:在事件处理函数中,this指向触发事件的元素。
// 事件处理函数中的 this
const button = document.createElement("button");
button.onclick = function() {
console.log(this); // 输出:button
};
例:
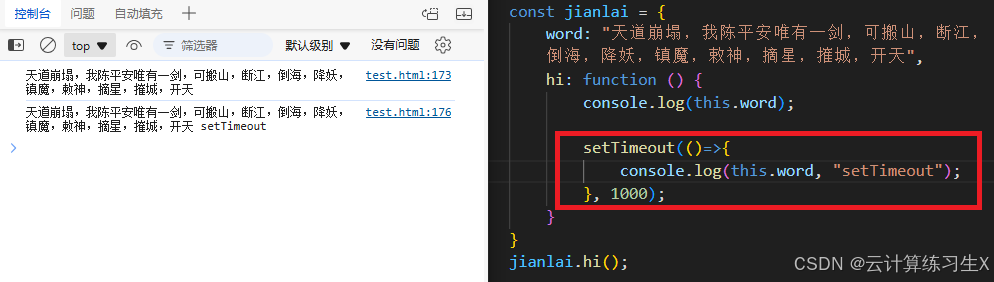
- 箭头函数中的
this:箭头函数没有自己的this,它会捕获上一层非箭头函数的this值。
// 箭头函数中的 this
const obj2 = {
func: () => {
console.log(this);
}
};
obj2.func(); // 输出:Window(浏览器环境)或 global(Node.js 环境)
例:
需要注意的是,this 的值是在运行时确定的,而不是在编写代码时确定的。因此,在编写代码时,需要注意函数的调用方式,以确保 this 的值是预期的。
2.10、小结
- 注释:单行
//, 多行/* */ - 输入输出语句:prompt()、alert()、console.log()、document.write()
- 变量和常量:let、const
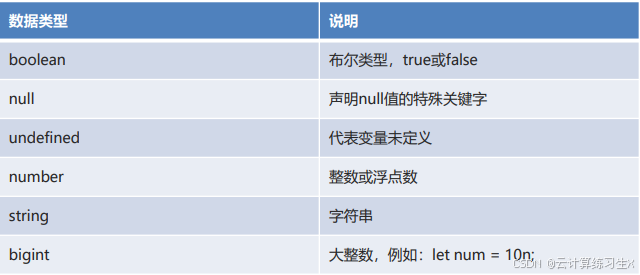
- 数据类型:boolean、null、undefined、number、string、bigint
- typeof 关键字:用于判断变量的数据类型
- 运算符:算数、赋值、逻辑、比较、三元运算符
- 流程控制和循环语句:if、switch、for、while
- 数组:数据类型和长度没有限制,
let 数组名 = [长度/元素] - 函数:类似方法,抽取代码,提高复用性