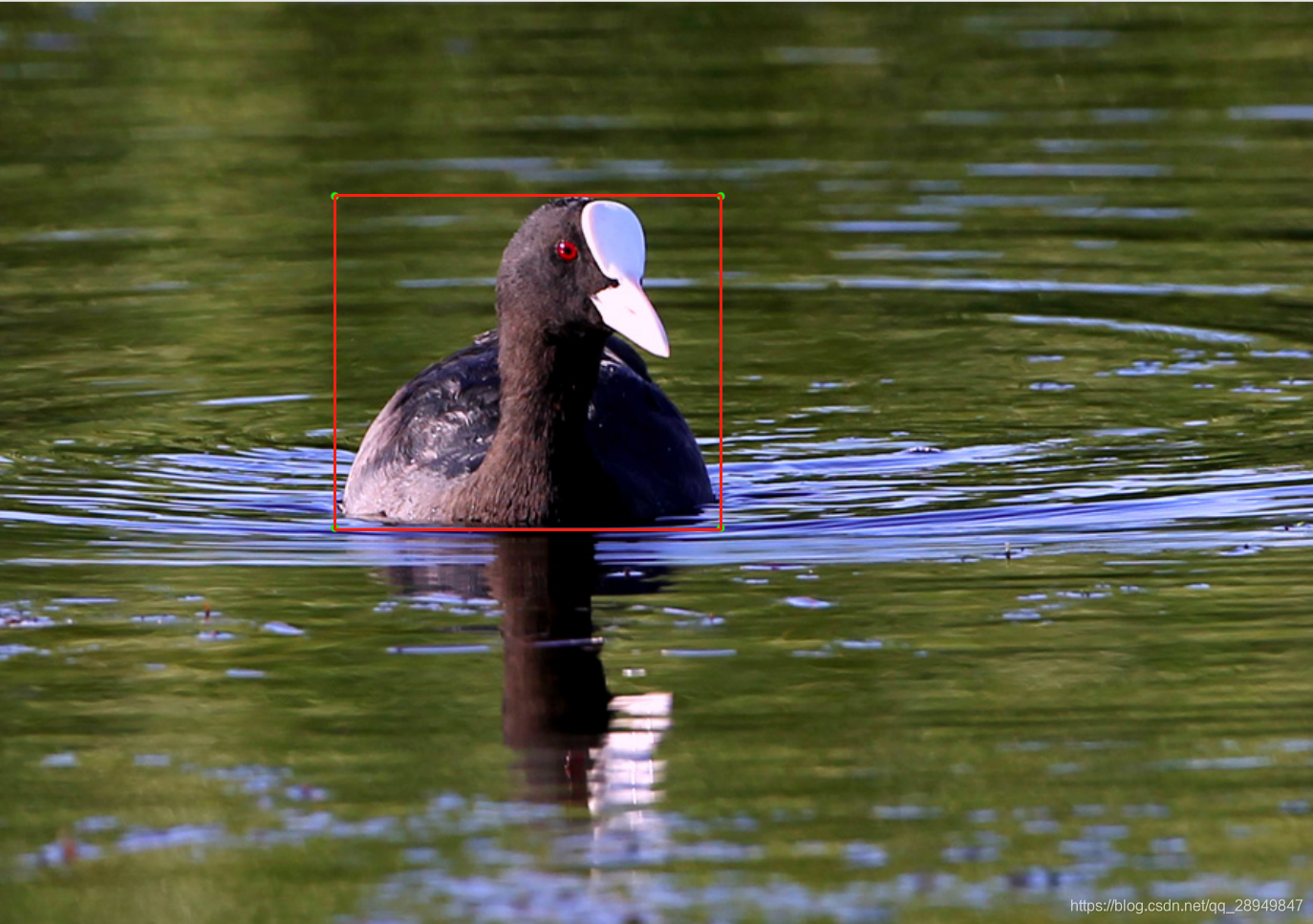
图片进行了resize后,对于标记框box进行相应的改变,与resize后的图片进行相对应。代码如下:
# 18233275213微信交流
import math
import os
from PIL import Image, ImageDraw
import numpy as np
import xml.etree.ElementTree as ET
def get_random_data(filename_jpg, box, nw, nh):
"""
修改 box
:param filename_jpg: 图片名
:param box: 原box
:param nw: 改变后的宽度
:param nh: 改变后的高度
:return:
"""
image = Image.open(filename_jpg)
iw, ih = image.size
# 对图像进行缩放并且进行长和宽的扭曲
image = image.resize((nw, nh), Image.BICUBIC)
# 将box进行调整
box_resize = []
for boxx in box:
boxx[0] = str(int(int(boxx[0]) * (nw / iw)))
boxx[1] = str(int(int(boxx[1]) * (nh / ih)))
boxx[2] = str(int(int(boxx[2]) * (nw / iw)))
boxx[3] = str(int(int(boxx[3]) * (nh / ih)))
box_resize.append(boxx)
return image, box_resize
def get_random_data_graybar(filename_jpg, box, w, h):
# ------------------------------#
# 读取图像并转换成RGB图像
# ------------------------------#
image = Image.open(filename_jpg)
# image = cvtColor(image)
# ------------------------------#
# 获得图像的高宽与目标高宽
# ------------------------------#
iw, ih = image.size
scale = min(w / iw, h / ih)
nw = int(iw * scale)
nh = int(ih * scale)
dx = (w - nw) // 2
dy = (h - nh) // 2
# ---------------------------------#
# 将图像多余的部分加上灰条
# ---------------------------------#
image = image.resize((nw, nh), Image.BICUBIC)
new_image = Image.new('RGB', (w, h), (128, 128, 128))
new_image.paste(image, (dx, dy))
box_resize = []
for boxx in box:
boxx[0] = str(int(int(boxx[0]) * (nw / iw) + dx))
boxx[1] = str(int(int(boxx[1]) * (nh / ih) + dy))
boxx[2] = str(int(int(boxx[2]) * (nw / iw) + dx))
boxx[3] = str(int(int(boxx[3]) * (nh / ih) + dy))
box_resize.append(boxx)
return new_image, box_resize
def read_xml(xml_name):
"""
看原xml中的box
:param xml_name: xml文件名
:return:
"""
etree = ET.parse(xml_name)
root = etree.getroot()
box = []
for obj in root.iter('object'):
xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax = (x.text for x in obj.find('bndbox'))
box.append([xmin,ymin,xmax,ymax])
return box
def write_xml(xml_name,save_name, box, resize_w, resize_h):
"""
将修改后的box 写入到 xml文件中
:param xml_name: 原xml
:param save_name: 保存的xml
:param box: 修改后需要写入的box
:return:
"""
etree = ET.parse(xml_name)
root = etree.getroot()
# 修改图片的宽度、高度
for obj in root.iter('size'):
obj.find('width').text = str(resize_w)
obj.find('height').text = str(resize_h)
# 修改box的值
for obj, bo in zip(root.iter('object'), box):
for index, x in enumerate(obj.find('bndbox')):
x.text = bo[index]
etree.write(save_name)
def start(sourceDir, targetDir, resize_w, resize_h):
"""
程序开始的主函数
:param sourceDir: 源文件夹
:param targetDir: 保存文件夹
:param resize_w: 改变后的宽度
:param resize_h: 改变后的高度
:return:
"""
for root, dir1, filenames in os.walk(sourceDir):
for filename in filenames:
file = os.path.splitext(filename)[0]
if os.path.splitext(filename)[1] == '.jpg':
print('正在进行resize:' + filename)
filename_jpg = os.path.join(root, filename)
xml_name = os.path.join(root, file + '.xml')
box = read_xml(xml_name)
# 灰度条填充,等比例
image_data, box_data = get_random_data_graybar(filename_jpg, box, resize_w, resize_h)
# 不填充直接resize, 会出现形变
# image_data, box_data = get_random_data(filename_jpg, box, resize_w, resize_h)
# 保存返回的图片
image_data.save(os.path.join(targetDir, filename))
# 查看修改后的结果,图片显示
for j in range(len(box_data)):
thickness = 3
left, top, right, bottom = box_data[j][0:4]
draw = ImageDraw.Draw(image_data)
for i in range(thickness):
draw.rectangle([int(left) + i, int(top) + i, int(right) - i, int(bottom) - i], outline=(255, 0, 0))
# 修改xml文件(将修改后的 box 写入到xml文件中)
save_xml = os.path.join(targetDir, file + '.xml')
write_xml(xml_name, save_xml, box_data, resize_w, resize_h)
# 查看box绘制在图片上的效果
path = './draw_img'
image_data.save(os.path.join(path, filename))
if __name__ == "__main__":
# 源文件夹
sourceDir = "./data/"
# 结果保存文件夹
targetDir = "./result/"
start(sourceDir, targetDir, 400, 400)
print('完成!')
效果演示:
实际图片:
shape:(900,631)
resize后的图片:
shape:(300,300)
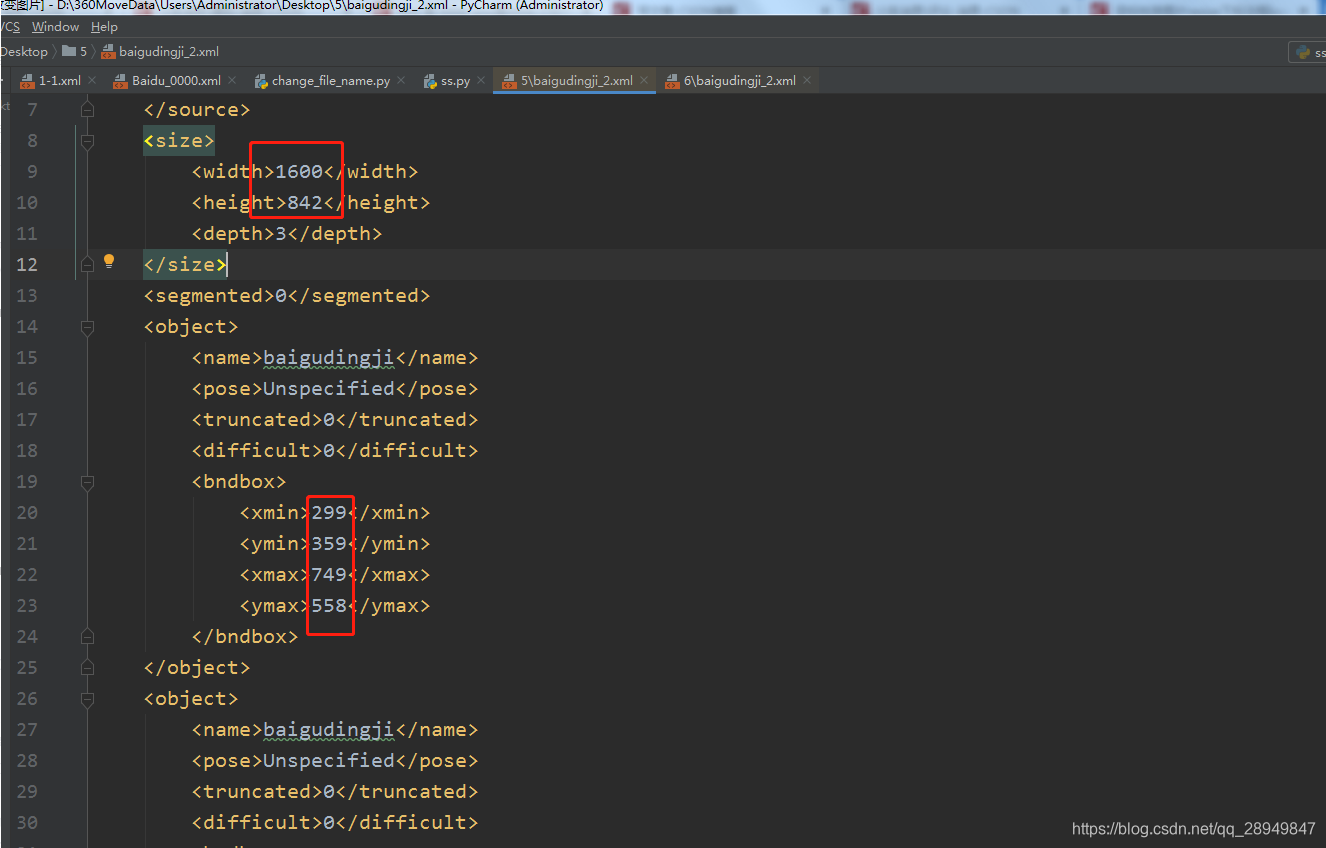
修改前的xml:
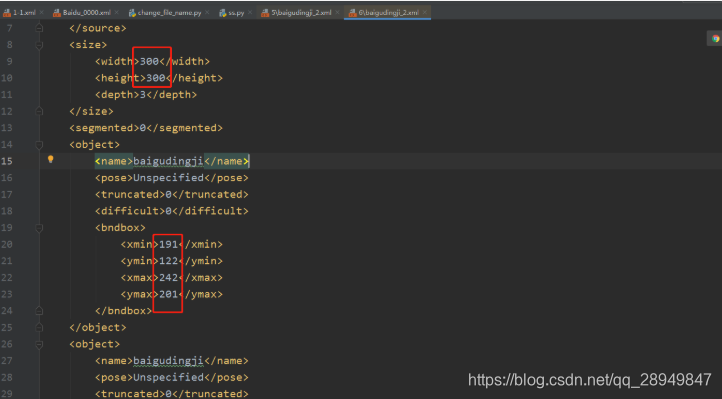
修改后的xml:
其实上面那种简单粗暴的resize并不是最好的结果,通过上面的resize,图片进行了拉伸,学出来的特征也会有问题,很难保证其准确性。这时候我们需要另外一种resize方式,不改变图片的长宽比,但是可以让图片尽可能的填充目标形状。这就会死LetterBox,这个是Yolo系列检测算法里面特有,但是同样也适用于任何一个检测算法。后面的文章会进行更新说明。
2022.02.12 更新get_random_data_graybar(filename_jpg, box, w, h) 无形变resize