Java NIO: Channels and Buffers(通道和缓冲区)
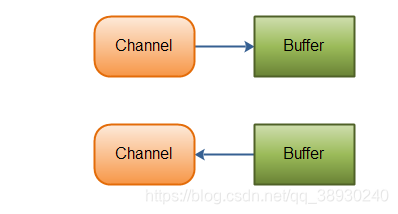
标准IO基于字节字符流,NIO基于Channel(通道)和缓冲区(Buffer),数据读操作是从通道读取到缓冲区,写操作是缓冲区写道通道。
Java NIO: Non-blocking IO(非阻塞IO)
Java NIO可以让你非阻塞的使用IO,例如:当线程从通道读取数据到缓冲区时,线程还是可以进行其他事情。当数据被写入到缓冲区时,线程可以继续处理它。从缓冲区写入通道也类似。
Java NIO: Selectors(选择器)
Java NIO引入了选择器的概念,选择器用于监听多个通道的事件(比如:连接打开,数据到达)。因此,单个的线程可以监听多个Channel。
Channel
| boolean isOpen();
void close() throws IOException; |
Java NIO中最重要的Channel的实现:
以下是Java NIO里关键的Buffer实现:
这些Buffer覆盖了你能通过IO发送的基本数据类型:byte, short, int, long, float, double 和 char。
例子:
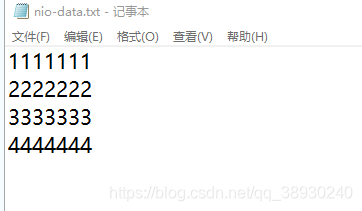
读取文件(多次取水)
| import java.io.File; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.RandomAccessFile; import java.nio.ByteBuffer; import java.nio.channels.FileChannel;
public class ChannelTest {
public static void main(String args[]){
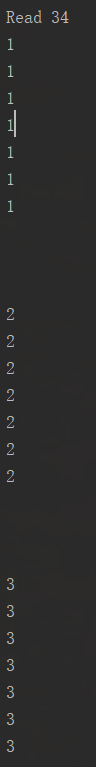
File file = new File("d:\\cxy\\nio-data.txt"); // RandomAccessFile: // 1.对文件内容(读操作和写操作)的访问 // 2.支持随机访问文件,以及访问文件的任意位置 // 硬盘存储上文件存储的方式为byte数据的集合 // 打开方式 rw(读写) 和 r(只读) try( RandomAccessFile accessFile = FileUtil.createRandomAccessFile(file, FileModeEnum.rw); FileChannel inChannel = accessFile.getChannel(); ){ ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocate(48);//capacity=48bytes int bytesRead = inChannel.read(buf); while (bytesRead != -1){ System.out.println("Read " + bytesRead); buf.flip();//反转buffer,再从缓冲里读取数据 //Q:为什么要反转?A:容量48,当前34,buf.hasRemaining()是false的 while (buf.hasRemaining()){ System.out.println((char) buf.get()); } buf.clear(); bytesRead = inChannel.read(buf); }
}catch (IOException e){
} } } |
说明: 1的ascii是49, 另外每行后面还有回车符(13,也叫归位符)和换行符(10),所以一共读了34个字节。
map()方法:MappedByteBuffer map(FileChannle.MapMode mode,long position,long size)
Parm1:映射模式:只读,读写等
Parm2,parm3:控制哪些数据映射成ByteBuffer
Ex:将FileChannel的全部数据映射为ByteBuffer:(一次取水)
| File f = new File("Test.java"); try( //通过文件输入流创建 FileChannel in = new FileInputStream(f).getChannel(); //通过文件输出流创建 FileChannel out = new FileOutputStream(f).getChannel();){
//将FileChannel的全部数据映射为ByteBuffer MappedByteBuffer buf = in.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY,0,f.length()); //使用utf-8编码 out.write(buf,"utf-8"); //clear();变为写模式 buf.clear(); Charset charset = Charset.forNmae("utf-8"); //utf-8解码器 CharsetDecoder decoder = charset.newDecoder(); //将ByteBUffer转为CharBuffer CharBuffer charBuffer = decoder.decode(buf); System.out.println(charBuffer.toString); ) catch(IOException e){ e.printStackTrace(); }
|
- ByteBuffer
- CharBuffer
- DoubleBuffer
- FloatBuffer
- IntBuffer
- LongBuffer
- ShortBuffer
- FileChannel 从文件中读写数据
- DatagramChannel 能通过UDP读写网络中的数据。
- SocketChannel 能通过TCP读写网络中的数据
- ServerSocketChannel 可以监听新进来的TCP连接,像Web服务器那样。对每一个新进来的连接都会创建一个SocketChannel。
- NIO的Channel ,可以从Channel中读数据,也可以写数据到通道,但IO的inputstream,outstream都是单向的。
- Channle中可以异步的读写。
- Channel中的数据要先读到一个Buffer,或者从一个Buffer写
- Channel提供了map()方法,可以将一块数据映射到内存.IO面向流,NIO面向块