目录
一、概述
ICP(Iterative Closest Point)配准算法是一种用于对齐两个点云的经典算法。其目标是通过迭代优化,使得源点云与目标点云之间的距离最小化。在这个过程中,优化的关键是设计一个合适的损失函数,并通过优化该损失函数来获得最优的变换矩阵(包括旋转和平移)。
1.1ICP的基本步骤
- 初始化:选择一个初始变换(通常是单位矩阵)将源点云与目标点云进行初步对齐。
- 最近点配对:对于源点云中的每个点,找到目标点云中的最近点作为对应点。
- 计算误差:使用损失函数计算源点与对应点之间的误差。
- 最小化误差:通过优化方法最小化误差,获得新的刚体变换(旋转和平移)。
- 应用变换:对源点云应用计算得到的刚体变换。
- 迭代:重复步骤2到步骤5,直到误差收敛或达到最大迭代次数。
1.2损失函数的设计
在ICP配准中,损失函数通常是源点云与目标点云之间的距离。根据距离的不同定义,可以设计不同的损失函数。
二、代码实现
2.1关键函数
目前,鲁棒核函数优化改进的ICP算法,仅为PointToPlane ICP提供了实现接口。registration_icp可以用参TransformationEstimationPointToPlane(loss)来调用。在TransformationEstimationPointToPlane(loss)的内部,实现了一个根据所提供的鲁棒核计算点到平面ICP目标的加权残差和雅可比矩阵。其中loss是一个给定的loss函数(也称为鲁棒核函数),具有如下几种形式:CauchyLoss、GMLoss、HuberLoss、L1Loss、L2Loss、TukeyLoss。此处以L2Loss函数为例,给出调用方式:
loss = o3d.pipelines.registration.L2Loss()2.2完整代码
import copy
import open3d as o3d
import numpy as np
# -------------------读取点云数据--------------------
source = o3d.io.read_point_cloud("hand.pcd")
target = o3d.io.read_point_cloud("hand_trans.pcd")
# --------------------计算法向量---------------------
source.estimate_normals(search_param=o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=0.01, max_nn=30))
target.estimate_normals(search_param=o3d.geometry.KDTreeSearchParamHybrid(radius=0.01, max_nn=30))
# ----------------可视化点云初始位置-----------------
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([source, target], width=600, height=600, mesh_show_back_face=False)
threshold = 1 # 距离阈值
trans_init = np.asarray([[ 0.98194534, -0.18295687, -0.04806395, 0.65088957],
[ 0.11626176, 0.78413388, -0.60960419, 4.19087836],
[ 0.14921985, 0.59300999, 0.79124749, 0.42555584],
[ 0, 0, 0, 1 ]]) # 初始变换矩阵,一般由粗配准提供
print("Initial alignment")
evaluation = o3d.pipelines.registration.evaluate_registration(source, target, threshold, trans_init)
print(evaluation) # 这里输出的是初始位置的 fitness和RMSE
print("Apply point-to-plane ICP")
loss = o3d.pipelines.registration.L2Loss() # ***************鲁棒核函数的调用方法******************
icp_p2plane = o3d.pipelines.registration.registration_icp(
source, target, threshold, trans_init,
o3d.pipelines.registration.TransformationEstimationPointToPlane(loss), # **********调用方法***********
o3d.pipelines.registration.ICPConvergenceCriteria(max_iteration=30)) # 设置最大迭代次数
print(icp_p2plane) # 输出ICP相关信息
print("Transformation is:")
print(icp_p2plane.transformation) # 输出变换矩阵
# -----------------可视化配准结果---------------------
def draw_registration_result(source, target, transformation):
source_temp = copy.deepcopy(source) # 由于函数transformand paint_uniform_color会更改点云,
target_temp = copy.deepcopy(target) # 因此调用copy.deepcoy进行复制并保护原始点云。
source_temp.paint_uniform_color([1, 0, 0]) # 点云着色
target_temp.paint_uniform_color([0, 1, 0])
source_temp.transform(transformation)
# o3d.io.write_point_cloud("trans_of_source1.pcd", source_temp) # 保存点云
o3d.visualization.draw_geometries([source_temp, target_temp], width=600, height=600, mesh_show_back_face=False)
draw_registration_result(source, target, icp_p2plane.transformation)三、实现效果
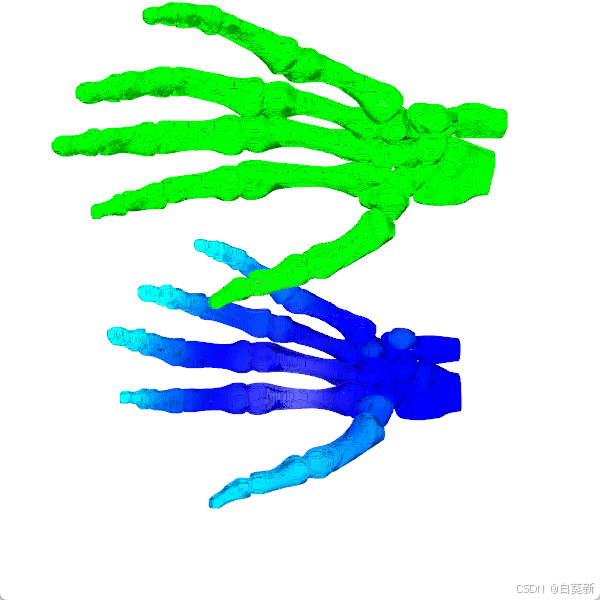
3.1原始点云
3.2配准后点云
3.3计算数据
Initial alignment
RegistrationResult with fitness=1.000000e+00, inlier_rmse=1.838722e-01, and correspondence_set size of 327323
Access transformation to get result.
Apply point-to-plane ICP
RegistrationResult with fitness=1.000000e+00, inlier_rmse=1.660569e-07, and correspondence_set size of 327323
Access transformation to get result.
Transformation is:
[[ 1.00000001e+00 3.24158898e-10 5.54218023e-09 -3.07668011e-08]
[ 1.41976914e-09 7.07106784e-01 -7.07106783e-01 4.99999999e+00]
[-7.42239700e-10 7.07106783e-01 7.07106780e-01 1.00000000e+00]
[ 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 0.00000000e+00 1.00000000e+00]]