## 基本介绍
离散化:把无限空间中有限的个体映射到有限的空间中去,以此提高算法的时空效率。通俗的说,离散化是在不改变数据相对大小的条件下,对数据进行相应的缩小。
适用范围:数组中元素值域很大,但个数不是很多。
比如将a[]=[1,3,100,2000,500000]映射到[0,1,2,3,4]这个过程就叫离散化。
离散化常与差分、前缀和、数组数组、线段树结合考查。
离散化模板
离散化有两个实现方式:
1、手写离散化
例如:对于序列 [105,35,35,79,-7],排序并去重后变为 [-7,35,79,105],由此就得到了对应关系 -7->1, 35->2, 79->3, 105->4。
基本的步骤可以分为:
1、用一个辅助的数组把你要离散的所有数据存下来。
2、排序,排序是为了后面的二分。
3、去重,因为我们要保证相同的元素离散化后数字相同。
4、索引,再用二分把离散化后的数字放回原数组。
vector<int> alls; // 存储所有待离散化的值
sort(alls.begin(), alls.end()); // 将所有值排序
alls.erase(unique(alls.begin(), alls.end()), alls.end()); // 去掉重复元素
// 二分求出x对应的离散化的值
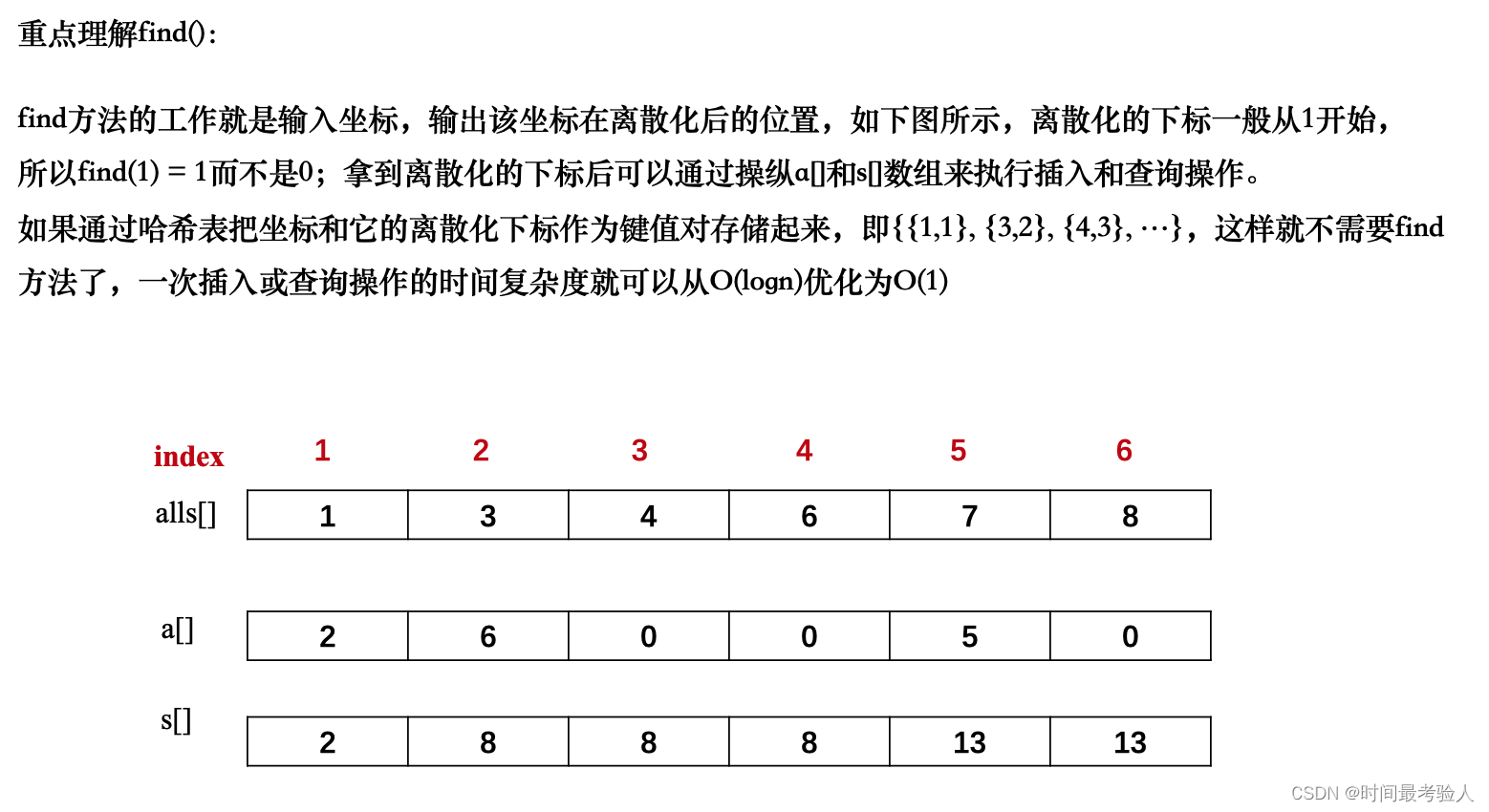
int find(int x) // 找到第一个大于等于x的位置
{
int l = 0, r = alls.size() - 1;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (alls[mid] >= x) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r + 1; // +1:映射到1, 2, ...n(不加的话就是0~n-1)
}
非vector版本:
(从1开始输入的话vector不方便)
#include<algorithm> // 头文件
const int MAXN = 1e6+4;
//n 原数组大小 num 原数组中的元素 lsh 离散化的数组 cnt 离散化后的数组大小
int lsh[MAXN], cnt, num[MAXN], n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++)
{
scanf("%d", &num[i]);
lsh[i] = num[i];
}
sort(lsh + 1 , lsh + n + 1);//排序
cnt = unique(lsh + 1, lsh + n + 1) - lsh - 1;//去重
// 二分求出x对应的离散化的值
int find(int x) // 找到第一个大于等于x的位置
{
int l = 1, r = cnt;
while (l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if (alls[mid] >= x) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r; // 映射到1, 2, ...n
}
【知识点】
对于随机给定的一个数组,去除其中所包含的重复元素可以通过调用C++的库函数unique来实现。
但有一点需要注意的是,unique仅是对相邻的重复元素进行去重,若要对随机给定的数组进行去重则需要先对数组进行排序,使得重复元素相邻.
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
int n = 10;
int a[10] = {4, 7, 4, 7, 2, 4, 6, 7, 4, 2};
sort(a, a + n);
int m = unique(a, a + n) - a;// 从0开始
cout << "数组新的长度 " << m << endl;
cout << "新数组 ";
for(int i = 0;i < m; ++i)
{
cout << ' ' << a[i];
}
return 0;
}
数组新的长度 4
新数组 2 4 6 7
注意事项:
1、去重并不是把数组中的元素删去,而是重复的部分元素在数组末尾,去重之后数组的大小要减一。
2、二分的时候,注意二分的区间范围,一定是离散化后的区间。
3、如果需要多个数组同时离散化,那就把这些数组中的数都用数组存下来。
2、map映射
(由于不需要排序和去重等操作,会比第一种好写,且代码量会少很多):可以用 map(每次在map中查询一下这个值是否存在,如果存在则返回对应的值,否则对应另一个值)或 hash表(即unordered_map或手写hash表,运用方式和map相同)。
map与unordered_map的区别
- 对于map的底层原理,是通过红黑树(一种非严格意义上的平衡二叉树)来实现的,因此map内部所有的数据都是有序的(默认按key进行升序排序),map的查询、插入、删除操作的时间复杂度都是O(logn)。
- unordered_map和map类似,都是存储的key-value的值,可以通过key快速索引到value。不同的是unordered_map不会根据key的大小进行排序,存储时是根据key的hash值判断元素是否相同,即unordered_map内部元素是无序的。unordered_map的底层是一个防冗余的哈希表(开链法避免地址冲突)。
巩固练习
电影
【题目链接】
步骤:
1、用 alls数组收集所有语言。
2、对 alls数组排序、去重。
3、find 函数用于把原始的稀疏编号转变为稠密编号。
4、ans 数组记录每种语言的科学家数。即这门语言有多少科学家会。
5、遍历所有电影,以每部电影的语音语言为条件,在ans数组中找最大值,若有多个相同的最大值,就找字幕语言最多的。
【代码实现】
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int a[N], b[N], c[N];
int ans[N * 3];//3*N是因为语言的来源有3个地方,假设都不相同,则有3*N种语言
vector<int> alls;
int n, m;
int find(int x)
{
int l = 0, r = alls.size() - 1;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(alls[mid] >= x) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )//保存科学家会的语言
{
cin >> a[i];
alls.push_back(a[i]);
}
cin >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ )
{
cin >> b[i];
alls.push_back(b[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ )
{
cin >> c[i];
alls.push_back(c[i]);
}
// 排序 + 去重
sort(alls.begin(), alls.end());
alls.erase(unique(alls.begin(), alls.end()), alls.end());
//a[i]中保存原始的稀疏编号,用find转变成稠密编号,并用ans数组记录每种语言出现的次数。
for(int i = 0; i < n; i ++) ans[find(a[i])]++;
//遍历所有电影,按要求找到最多科学家会的电影
int ans0 = 0, ans1 = 0, ans2 = 0;
//ans0保存最终结果,ans1和ans2为中间结果
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ )
{
//会第i个电影音频的科学家数;会第i个电影字幕的科学家数
int anx = ans[find(b[i])];
int any = ans[find(c[i])];
// 前者判断条件表示有电影刷新
// 后者判断条件表示相同电影条件下的字幕刷新
if(anx > ans1 || (anx == ans1 && any > ans2))
{
ans0 = i + 1;// 我们下标从0开始的
ans1 = anx;
ans2 = any;
}
}
if(ans0 == 0) puts("1");// 如果所有电影的音频和字幕科学家都不懂,随便选一个电影
else cout << ans0;
return 0;
}
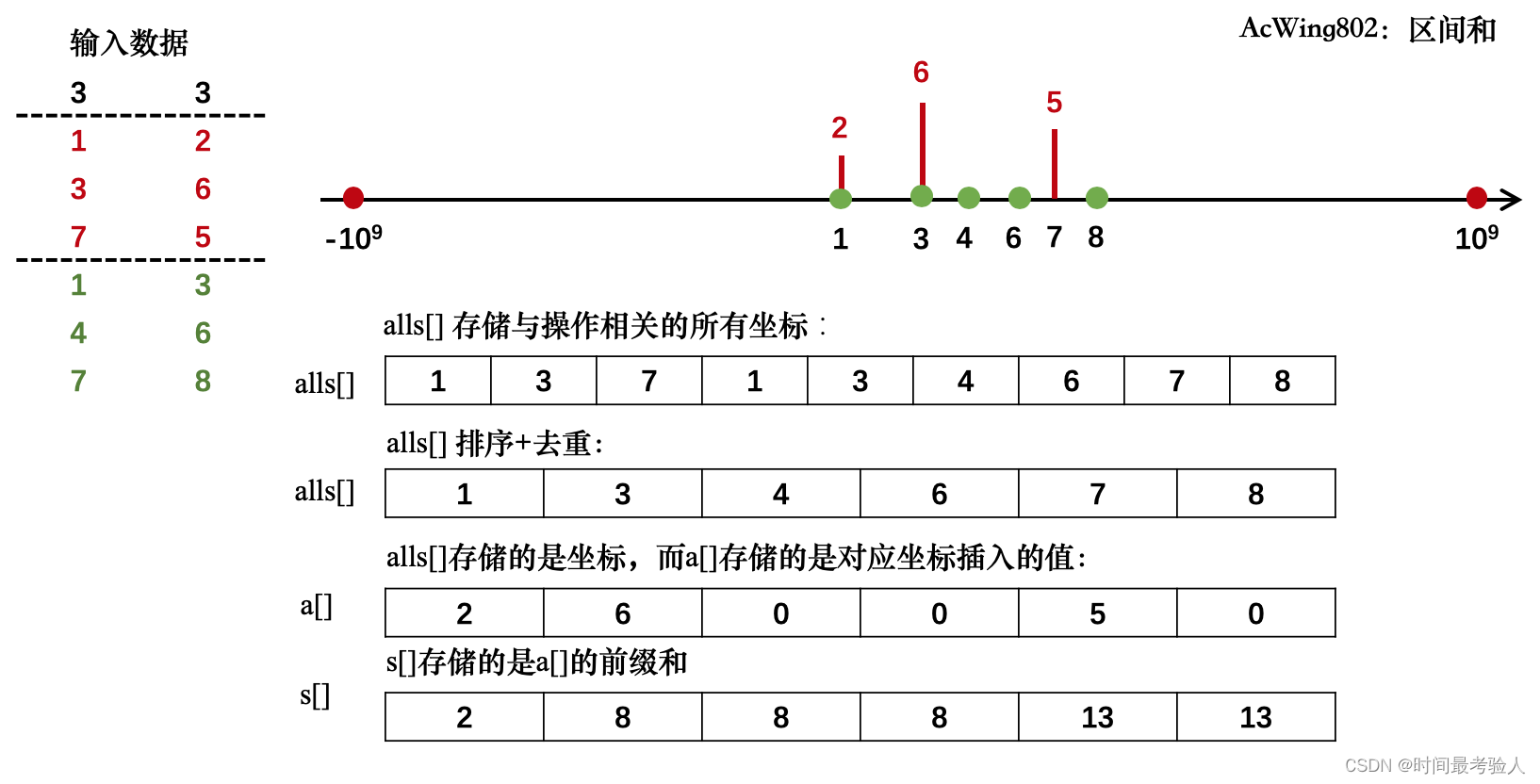
区间和
思路:值域很大用离散化压缩优化!
【代码实现】
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int N = 3e5 + 10;
int a[N], s[N];
vector<PII> add, query; // 方便我们离散化还原数值,和区间查询操作
vector<int> alls; // 存储数值进行离散化操作
int n, m;
// 二分求出x对应的离散化的值
int find(int x) // 找到第一个大于等于x的位置
{
int l = 0, r = alls.size() - 1;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(alls[mid] >= x) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r + 1;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
int x, c;
cin >> x >> c;
add.push_back({x, c});
alls.push_back(x);
}
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ )
{
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
query.push_back({l, r});
alls.push_back(l);
alls.push_back(r);
}
// 排序 + 去重
sort(alls.begin(), alls.end());
alls.erase(unique(alls.begin(), alls.end()), alls.end());
// 数值还原映射到a[]数组
for(auto item : add)
{
int x = find(item.x);// 找到映射后的位置
a[x] += item.y;// 插入数值
}
// 预处理前缀和
for (int i = 1; i <= alls.size(); i ++ ) s[i] = s[i - 1] + a[i];
// 处理区间和
for(auto item : query)
{
// 找到离散化后对应的位置
int l = find(item.x), r = find(item.y);
cout << s[r] - s[l - 1] << endl; // 前缀和求区间和
}
return 0;
}
金发姑娘和 N 头牛
【题目链接】1952. 金发姑娘和 N 头牛 - AcWing题库
区间和的应用题
m:20000
n:1e^9
裸差分O(n + m)会爆炸,长度虽然很长但绝大部分的点都用不到,因此可以用离散化进行压缩
【代码实现】
map实现离散化:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int INF = 2e9;
int n, x, y, z;
int main()
{
map<int, int> b; // 离散化及差分数组
cin >> n >> x >> y >> z;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
//给三个大区间 + c
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
//[-INF,r)
b[-INF] += x;
b[l] -= x;
//[l, r]
b[l] += y;
b[r + 1] -= y;
//b(r, INF]
b[r + 1] += z;
b[INF] -= z;
}
int res = 0, sum = 0;
// 枚举差分数组,求前缀和,更新最大值
for(auto& [k, v] : b)// map的遍历方式
{
sum += v;// 前缀和
res = max(res, sum);
}
/*for(auto item : b)// 这样遍历也可以
{
sum += item.second;// 前缀和
res = max(res, sum);
}
*/
cout << res;
return 0;
}
手写实现离散化:
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <map>
#include <algorithm>
#define x first
#define y second
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
typedef pair<int, int> PII;
const int INF = 2e9;
vector<PII> query;// 存储温度区间
vector<int> alls;// 存储离散化后的数值
int b[N * 2]; // 差分数组
int n, x, y, z;
int find(int x)
{
int l = 0, r = alls.size() - 1;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(alls[mid] >= x) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r;
}
int main()
{
cin >> n >> x >> y >> z;
alls.push_back(-INF), alls.push_back(INF);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
int l, r;
cin >> l >> r;
query.push_back({l, r});
alls.push_back(l);
alls.push_back(r);
}
// 排序 + 排重
sort(alls.begin(), alls.end());
alls.erase(unique(alls.begin(), alls.end()), alls.end());
// 枚举所有区间, 求出离散化后的值
for (auto item : query)
{
int l = find(item.x), r = find(item.y);
// -INF映射到下标0 INF映射到alls.szie()-1
b[0] += x;
b[l] -= x;
b[l] += y;
b[r + 1] -= y;
b[r + 1] += z;
b[alls.size() - 1] -= z;
}
// 枚举差分数组,求前缀和,更新最大值
int sum = 0, res = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < alls.size(); i ++ )
{
sum += b[i];
res = max(res, sum);
}
cout << res;
return 0;
}
粉刷栅栏
【题目链接】
线段覆盖
【题目链接】4195. 线段覆盖 - AcWing题库
思路:差分 + 离散化
- 一开始假设我们有一个横坐标区间轴,初始都为0,每每来一条线段,我们就给这条线内所有点的数值
+ 1,将所有线段操作完之后,统计一下最开始数组里边值为1、3、…的数有多少个。 - 回想裸差分坐标是直接用数组来存的,但本题的坐标范围达到10^18,因此不能用数组来存,而实际操作的点并不是很多(最多2n个),因此可以用离散化压缩(map实现)
【代码实现】
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <map>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 200010;
map<LL, int> b; //b是用map构建的差分数组,用来记录l,r
LL ans[N]; //ans代表答案数组,ans[i]即被i条线段覆盖的点有几个
int main()
{
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
for (int i = 0; i < n; i ++ )
{
LL l, r;
scanf("%lld%lld", &l, &r);
b[l] ++, b[r + 1] -- ; //构建差分
}
LL sum = 0, last = -1; //sum记录的是如今重叠的次数,last记录上一个点(便于相减求中间点的数量
for (auto& [k, v]: b) //枚举map中的点
{
if (last != -1) ans[sum] += k - last;
sum += v;
last = k; //记录一下现在的点
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) //输出结果
printf("%lld ", ans[i]);
return 0;
}
逆序对
【代码实现】
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <vector>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
const int N = 1e8 + 10;
typedef long long LL;
int len;
int a[N];
int tr[N];
// vector<int> alls;
int alls[N];
int find(int x)
{
int l = 1, r = len;
while(l < r)
{
int mid = l + r >> 1;
if(alls[mid] >= x) r = mid;
else l = mid + 1;
}
return r;
}
int lowbit(int x) // 返回末尾的1
{
return x & -x;
}
//这个树状数组的下标是数的范围,不是题中的n,数的个数的范围。
void add(int idx, int c)
{
for(int i = idx; i <= len; i += lowbit(i)) tr[i] += c;
}
int sum(int x)
{
int res = 0;
for (int i = x; i ; i -= lowbit(i)) res += tr[i];
return res;
}
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
cin >> a[i];
alls[i] = a[i];
}
// 排序 + 去重
sort(alls + 1, alls + 1 + n);
len = unique(alls + 1, alls + 1 + n) - alls - 1;// 去重后的长度
LL res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ )
{
int x = find(a[i]);
res += sum(len) - sum(x);
add(x, 1);
}
cout << res;
return 0;
}
程序自动分析
【题目链接】[P1955 NOI2015] 程序自动分析 - 洛谷 | 计算机科学教育新生态 (luogu.com.cn)
思路:
分析一下上面的举例,我们可以发现这组约束条件中“相等”的约束条件可以看做是一个并查集合并的过程,如x1=x2,相当于是将x1,x2合并到一个集合的操作,而“不等”的约束条件,如x1≠x4相当于是在说x1和x4不属于一个集合。
首先,对于约束条件的配置顺序我们是不关心的,换句话说,顺序不会影响我们最终的结果,因此我们可以先考虑相等的情况:xi=xj(这些情况当然不可能有矛盾),再考虑不等的情况:xi!=xj,如果根据之前相等的情况已经可以推出xi=xj,即xi、xj两者已经在同一集合中了,则表明有矛盾。
离散化有两种写法:
第一种是保序:离散化前是什么大小关系,离散化后还是什么大小关系(排序、判重、二分,可用库函数来实现)。
第二种不要求保序(由于不需要排序和去重等操作,会比第一种好写,且代码量会少很多):可以用 map(每次在map中查询一下这个值是否存在,如果存在则返回对应的值,否则对应另一个值)或 hash表(即unordered_map或手写hash表,运用方式和map相同)。
unordered_map<int, int> S;
n = 0; //从第0个位置开始
// 离散化操作
int get(int x)
{
if(!S.count(x)) S[x] = ++ n;
return S[x];
}
步骤:
- 离散化。
- 将所有相等条件合并(并查集)。
- 依次判断每个不等条件(query)。
【代码实现】
#include <iostream>
#include <cstring>
#include <algorithm>
#include <unordered_map>
using namespace std;
const int N = 2e5 + 10;
int n, m;
int p[N];
unordered_map<int, int> S;
struct Query
{
int x, y, e;
}query[N];
// 离散化操作
int get(int x)
{
if(!S.count(x)) S[x] = ++ n;
return S[x];
}
int find(int x) // 并查集
{
if (p[x] != x) p[x] = find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
int T;
cin >> T;
while(T --)
{
n = 0;
S.clear(); //多组测试数据
cin >> m;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ )
{
int x, y, e;
cin >> x >> y >> e;
x = get(x), y = get(y); // 先离散化
query[i] = {x, y, e};
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i ++ ) p[i] = i; // 离散化后再初始化并查集
// 先合并相等的情况
for(int i = 0; i < m; i ++)
{
if(query[i].e == 1)
{
int pa = find(query[i].x), pb = find(query[i].y);
p[pa] = pb;
}
}
// 检查不相等的情况,看看是否矛盾
bool flag = false;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i ++ )
{
if(query[i].e == 0)
{
int pa = find(query[i].x), pb = find(query[i].y);
if(pa == pb)
{
flag = true;
break;
}
}
}
if(flag) puts("NO");
else puts("YES");
}
return 0;
}
部分内容学习转载:
- 作者:liangshang。链接:链接
- 作者:努力的老周。链接:离散化_努力中的老周的专栏-CSDN博客
参考文献:
- acwing算法基础课
- 洛谷题库