C++结构体
C++基础知识持续更新,今天来记录结构体的基本知识,包括结构体的定义和使用,结构体数组,结构体指针,结构体嵌套结构体,结构体做函数参数,结构体中的const的使用场景,以及结构体的案例。
1. 结构体的定义和使用
结构体属于用户自定义的数据类型,允许用户存储不同的数据类型。直接用实例展示语法:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//1.创建学生数据类型:学生包括(姓名,年龄,分数)
//自定义数据类型,一些类型集合组成的一个类型
//语法 struct 类型名称 {成员列表}
struct Student
{
//成员列表
//成员姓名
string name;
//成员年龄
int age;
//成员分数
int score;
}s3; //在定义结构体时顺便创建结构体变量
//2.通过学生类型创建具体学生
int main() {
//2.1 struct Student s1
struct Student s1;
//给s1属性赋值,通过.来访问结构体变量的属性
s1.name = "张三";
s1.age = 18;
s1.score = 100;
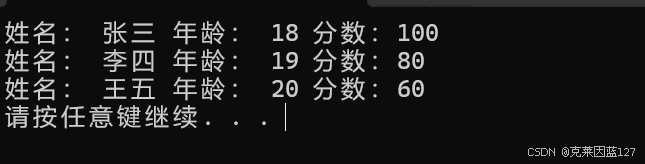
cout << "姓名: " << s1.name << " 年龄: " << s1.age << " 分数:" << s1.score << endl;
//2.2 struct Student s2 = {...........}
struct Student s2 = { "李四", 19, 80 };
cout << "姓名: " << s2.name << " 年龄: " << s2.age << " 分数:" << s2.score << endl;
//2.3在定义结构体时顺便创建结构体变量
s3.name = "王五";
s3.age = 20;
s3.score = 60;
cout << "姓名: " << s3.name << " 年龄: " << s3.age << " 分数:" << s3.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果如下:
2.结构体数组
作用:将自定义的结构体放入到数组中方便维护。
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//结构体数组
//1.定义结构体
struct Student
{
//成员列表
//成员姓名
string name;
//成员年龄
int age;
// //成员分数
int score;
};
int main() {
//2.创建一个结构体的数组
struct Student StuArray[3] =
{
{"张三", 18,100},
{"李四", 19 , 80},
{"王五", 20, 66}
};
//3.给结构体数组中的元素赋值
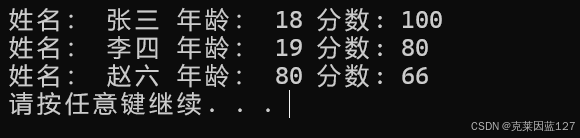
StuArray[2].name = "赵六";
StuArray[2].age = 80;
StuArray[2].score = 66;
//4.遍历结构体数组
for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++)
{
cout << "姓名: " << StuArray[i].name
<< " 年龄: " << StuArray[i].age
<< " 分数: " << StuArray[i].score << endl;
}
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结果显示如下:
3. 结构体指针:
作用:通过指针访问结构体中的成员
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//结构体指针
struct student
{
//成员列表
//成员姓名
string name;
//成员年龄
int age;
// //成员分数
int score;
};
int main() {
//1.创建学生结构体变量
struct student s = { "张三", 18, 100 };
//2.通过指针指向结构体变量
struct student* p = &s;//取s地址的时候返回的是定义时候的数据类型,即struct student
//3.通过指针访问结构体变量中的数据
//通过结构体指针访问结构体中的属性,要使用 -> 符号
cout << "姓名: " << p->name << " 年龄: " << p->age << " 分数: " << p->score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
结果如下:
4.结构体嵌套结构体
作用:结构体中的成员可以是另一个结构体
例如:每个老师辅导一个学生,一个老师的结构体中,记录一个学生的结构体
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//学生结构体
struct student
{
//成员列表
string name;//学生姓名
int age;//学生年龄
int score;//学生成绩
};
//教师结构体
struct teacher
{
//成员列表
int id;//教师编号
string name;//教师姓名
int age;//教师年龄
struct student stu;//子结构体 学生
};
int main() {
//结构体嵌套结构体
//创建老师
teacher t;
t.id = 1000;
t.name = "王老师";
t.age = 50;
t.stu.name = "小李";
t.stu.age = 20;
t.stu.score = 60;
cout << "老师姓名:" << t.name << " 老师编号:" << t.id << " 老师年龄:" << t.age
<< " 老师辅导的学生姓名:" << t.stu.name << " 学生年龄:" << t.stu.age
<< " 学生成绩:" << t.stu.score << endl;
system("pause");
return 0;
}
5.结构体做函数参数
结构体做函数参数作用:将结构体作为参数向函数中传递
传递方式有两种:值传递 地址传递
值传递
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
学生结构体
struct student
{
//成员列表
string name;//学生姓名
int age;//学生年龄
int score;//学生成绩
};
//打印学生信息
//1.值传递
void printStudent1(struct student s)
{
cout << " 子函数中学生信息 姓名: " << s.name << " 年龄: " << s.age << " 分数: " << s.score << endl;
}
int main() {
//结构体做函数参数
//将学生传入到一个参数中,打印学生身上的所有信息
//创建结构体变量
student s;
s.name = "张三";
s.age = 50;
s.score = 85;
//cout << "姓名: " << s.name << " 年龄: " << s.age << " 分数: " << s.score << endl;
printStudent1(s);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
地址传递
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
学生结构体
struct student
{
//成员列表
string name;//学生姓名
int age;//学生年龄
int score;//学生成绩
};
//打印学生信息
//1.值传递
void printStudent1(struct student s)
{
cout << " 子函数中学生信息 姓名: " << s.name << " 年龄: " << s.age << " 分数: " << s.score << endl;
}
//2.地址传递
void printStudent2(struct student *p)
{
cout << " 子函数2中学生信息 姓名: " << p->name << " 年龄: " << p->age << " 分数: " << p->score << endl;
}
int main() {
//结构体做函数参数
//将学生传入到一个参数中,打印学生身上的所有信息
//创建结构体变量
student s;
s.name = "张三";
s.age = 50;
s.score = 85;
//cout << "姓名: " << s.name << " 年龄: " << s.age << " 分数: " << s.score << endl;
//printStudent1(s);
printStudent2(&s);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
注意:如果不想修改主函数中的数据,用值传递;反之用地址传递
6.结构体中的const的使用场景
作用:用const来防止误操作
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//const的使用场景
struct student
{
//成员列表
string name;//学生姓名
int age;//学生年龄
int score;//学生成绩
};
//void printStudents(struct student s)
//{
// cout << "姓名: " << s.name << " 年龄: " << s.age << " 分数: " << s.score << endl;
//}
void printStudents(const student *s)
{
//s->age = 160;//加入const之后,一旦有修改就会报错,可以防止误操作
cout << "姓名: " << s->name << " 年龄: " << s->age << " 分数: " << s->score << endl;
}
int main() {
//创建结构体变量
struct student s = { "张三", 18, 100 };
//通过函数打印结构体变量信息
//printStudents(s);
printStudents(&s);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
7.结构体案例一 多名老师和多名学生
学校正在做毕设项目,每名老师带领5个学生,总共有3名老师,需求如下:
设计学生和老师的结构体,其中在老师的结构体中,有老师姓名和一个存放5名学生的数组作为成员学生的成员有姓名、考试分数,创建数组存放3名老师,通过函数给每个老师及所带的学生赋值最终打印出老师数据以及老师所带的学生数据。
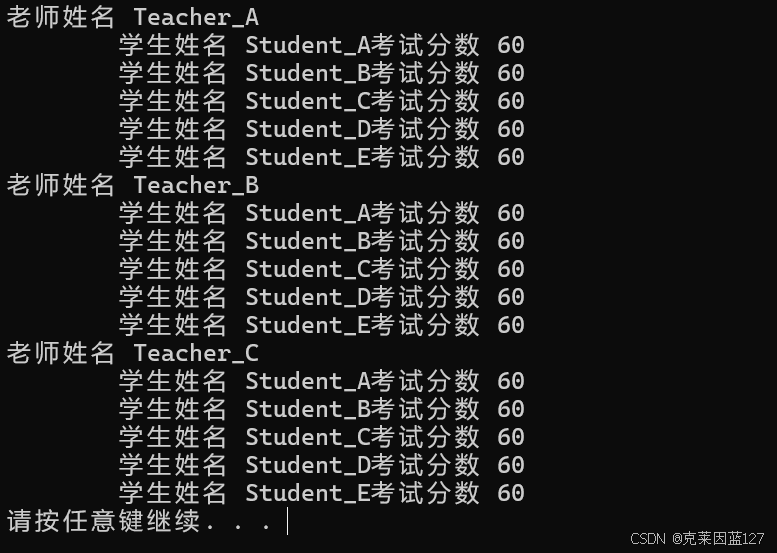
首先我们将所有学生的分数都设为60
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//学生的结构体
struct Student
{
string sName;
int score;
};
//老师的结构体定义
struct Teacher
{
string tName;
struct Student sArray[5];
};
//给老师和学生数组赋值的函数
void allocateSpace(struct Teacher tArray[], int len)
{
string nameSeed = "ABCDE";
//给老师开始赋值
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
tArray[i].tName = "Teacher_";
tArray[i].tName += nameSeed[i];
//通过循环给每位老师所带的学生赋值
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
tArray[i].sArray[j].sName = "Student_";
tArray[i].sArray[j].sName += nameSeed[j];
tArray[i].sArray[j].score = 60;
}
}
}
//创建打印所有信息的函数
void printInfo(struct Teacher tArray[], int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << "老师姓名 " << tArray[i].tName << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
cout << "\t学生姓名 " << tArray[i].sArray[j].sName <<
"考试分数 " << tArray[i].sArray[j].score << endl;
}
}
}
int main() {
//1.创建3名老师的数组
struct Teacher tArray[3];
//2.通过函数给三名老师的信息赋值,并给老师带的学生信息赋值
int len = sizeof(tArray) / sizeof(tArray[0]);
allocateSpace(tArray, len);
//3.打印所有老师及带的学生的信息
printInfo(tArray, len);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
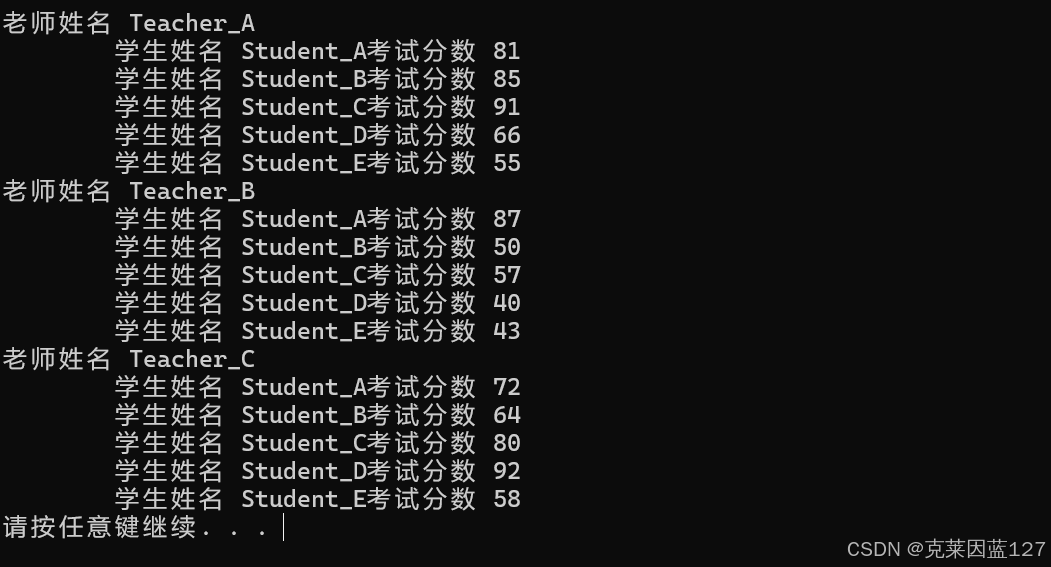
下面将分数改为一个随机值:
//通过循环给每位老师所带的学生赋值
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
tArray[i].sArray[j].sName = "Student_";
tArray[i].sArray[j].sName += nameSeed[j];
int random = rand() % 61 + 40;//40-100分区间
tArray[i].sArray[j].score = random;
}
输出结果:
但是,这样会带来一个弊端,会发现编译几次后总有一个同学出现同样的成绩,我们可以在程序中引入随机数种子来更新随机数
新增内容如下:
在头文件中添加#include<ctime>
在main函数中添加 srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
完整程序如下:
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
#include<ctime>
//学生的结构体
struct Student
{
string sName;
int score;
};
//老师的结构体定义
struct Teacher
{
string tName;
struct Student sArray[5];
};
//给老师和学生数组赋值的函数
void allocateSpace(struct Teacher tArray[], int len)
{
string nameSeed = "ABCDE";
//给老师开始赋值
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
tArray[i].tName = "Teacher_";
tArray[i].tName += nameSeed[i];
//通过循环给每位老师所带的学生赋值
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
tArray[i].sArray[j].sName = "Student_";
tArray[i].sArray[j].sName += nameSeed[j];
int random = rand() % 61 + 40;//40-100分区间
tArray[i].sArray[j].score = random;
}
}
}
//创建打印所有信息的函数
void printInfo(struct Teacher tArray[], int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << "老师姓名 " << tArray[i].tName << endl;
for (int j = 0; j < 5; j++)
{
cout << "\t学生姓名 " << tArray[i].sArray[j].sName <<
"考试分数 " << tArray[i].sArray[j].score << endl;
}
}
}
int main() {
//随机数种子
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
//1.创建3名老师的数组
struct Teacher tArray[3];
//2.通过函数给三名老师的信息赋值,并给老师带的学生信息赋值
int len = sizeof(tArray) / sizeof(tArray[0]);
allocateSpace(tArray, len);
//3.打印所有老师及带的学生的信息
printInfo(tArray, len);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
8.结构体案例二 冒泡法排序
案例需求:设计一个英雄的结构体,包括胧员姓名,年龄,性别;创建结构体数组,数组中存放5名英雄,
通过冒泡排序的算法,将数组中的英雄按照年龄进行升序排序,最终打印排序后的结果
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#include<string>
//1.创建英雄的结构体
struct Hero
{
string name;
int age;
string sex;
};
//冒泡排序实现年龄的升序排列
void bubbleSort(struct Hero heroArray[], int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len - 1; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < len - i - 1; j++)
{
//如果j小标的元素年龄大于j+ 1小标的元素的年龄,交换两个元素
if (heroArray[j].age > heroArray[j + 1].age)
{
struct Hero temp = heroArray[j];
heroArray[j] = heroArray[j + 1];
heroArray[j + 1] = temp;
}
}
}
}
//创建排序后数组的信息
void printHero(struct Hero heroArray[], int len)
{
for (int i = 0; i < len; i++)
{
cout << "姓名: " << heroArray[i].name << " 年龄: " << heroArray[i].age
<< " 性别: " << heroArray[i].sex << endl;
}
}
int main() {
//2.创建数组存放5名英雄
struct Hero heroArray[5] =
{
{"刘备", 23,"男"},
{"关羽", 22,"男"},
{"张飞", 20,"男"},
{"赵云", 21,"男"},
{"貂蝉", 19,"女"},
};
int len = sizeof(heroArray) / sizeof(heroArray[0]);
cout << "排序前的结果" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++)
{
cout << "姓名: " << heroArray[i].name << " 年龄: " << heroArray[i].age
<< " 性别: " << heroArray[i].sex << endl;
}
//3.对数组进行排序,按照年龄进行升序排列
bubbleSort(heroArray, len);
cout << "排序后的结果" << endl;
//4.将排序后的结果打印输出
printHero(heroArray, len);
system("pause");
return 0;
}
运行结果为:
更多知识推荐大家b站学习黑马程序员老师的c++课程,肯定会收获满满!