Elasticsearch是由elastic公司开发的一套搜索引擎技术,它是elastic技术栈中的一部分,提供核心的数据存储、搜索、分析功能
elasticsearch之所以有如此高性能的搜索表现,正是得益于底层的倒排索引技术。那么什么是倒排索引呢?
Elasticsearch搜索原理
正向索引
我们先来回顾一下正向索引。
例如有一张名为tb_goods的表:
| id | title | price |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 小米手机 | 3499 |
| 2 | 华为手机 | 4999 |
| 3 | 华为小米充电器 | 49 |
| 4 | 小米手环 | 49 |
| ... | ... | ... |
其中的id字段已经创建了索引,由于索引底层采用了B+树结构,因此我们根据id搜索的速度会非常快。但是其他字段例如title,只在叶子节点上存在。检查到搜索条件为like '%手机%',如果符合则放入结果集,不符合则丢弃。
综上,根据id精确匹配时,可以走索引,查询效率较高。而当搜索条件为模糊匹配时(模糊查询只有%在关键词前面索引才会失效),由于索引无法生效,导致从索引查询退化为全表扫描,效率很差。
因此,正向索引适合于根据索引字段的精确搜索,不适合基于部分词条的模糊匹配。而倒排索引恰好解决的就是根据部分词条模糊匹配的问题。
倒排索引
倒排索引中有两个非常重要的概念:
-
文档(
Document):用来搜索的数据,其中的每一条数据就是一个文档。例如一个网页、一个商品信息 -
词条(
Term):对文档数据或用户搜索数据,利用某种算法分词,得到的具备含义的词语就是词条。例如:我是中国人,就可以分为:我、是、中国人、中国、国人这样的几个词条
创建倒排索引是对正向索引的一种特殊处理和应用,流程如下:
-
将每一个文档的数据利用分词算法根据语义拆分,得到一个个词条
-
创建表,每行数据包括词条、词条所在文档id、位置等信息
-
因为词条唯一性,可以给词条创建正向索引
| 词条(索引) | 文档id |
|---|---|
| 小米 | 1,3,4 |
| 手机 | 1,2 |
| 华为 | 2,3 |
| 充电器 | 3 |
| 手环 | 4 |
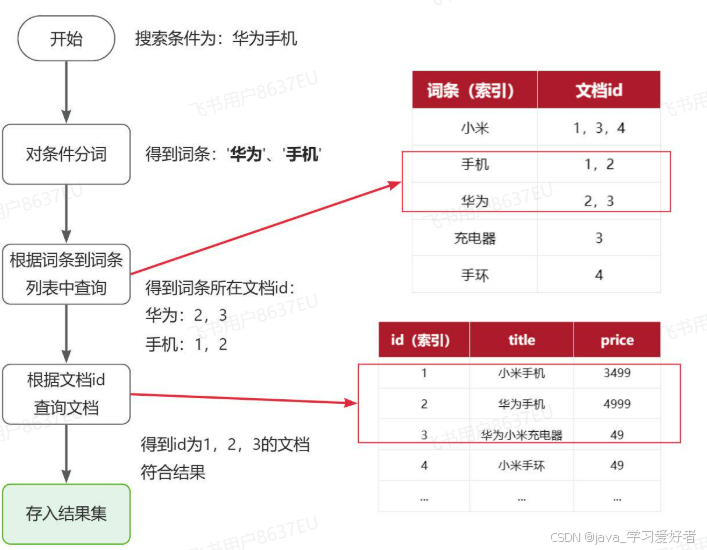
倒排索引的搜索流程如下(以搜索"华为手机"为例),如图
流程描述:
1)用户输入条件"华为手机"进行搜索。
2)对用户输入条件分词,得到词条:华为、手机。
3)拿着词条在倒排索引中查找(由于词条有索引,查询效率很高),即可得到包含词条的文档id:1、2、3。
4)拿着文档id到正向索引中查找具体文档即可(由于id也有索引,查询效率也很高)。
虽然要先查询倒排索引,再查询正排索引,但是无论是词条、还是文档id都建立了索引,查询速度非常快!无需全表扫描。
Elasticsearch安装
本项目采用docker部署
创建网络 es-net
docker network create es-net安装 elasticsearch
docker run -d \
--name es \
-e "ES_JAVA_OPTS=-Xms512m -Xmx512m" \
-e "discovery.type=single-node" \
-v es-data:/usr/share/elasticsearch/data \
-v es-plugins:/usr/share/elasticsearch/plugins \
--privileged \
--network es-net \
-p 9200:9200 \
-p 9300:9300 \
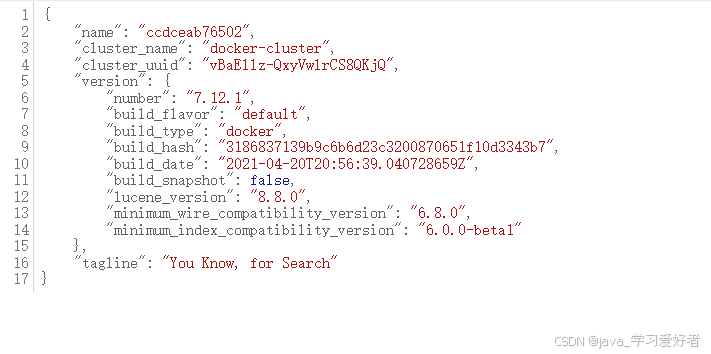
elasticsearch:7.12.1访问:http://服务器id:9200/ 若出现以下JSON数据,表示安装成功
kibana安装
Kibana是elastic公司提供的用于操作Elasticsearch的可视化控制台。它的功能非常强大,包括:
-
对Elasticsearch数据的搜索、展示
-
对Elasticsearch数据的统计、聚合,并形成图形化报表、图形
-
对Elasticsearch的集群状态监控
-
它还提供了一个开发控制台(DevTools),在其中对Elasticsearch的Restful的API接口提供了语法提示
部署Kibana
docker run -d \
--name kibana \
-e ELASTICSEARCH_HOSTS=http://es:9200 \
--network=es-net \
-p 5601:5601 \
kibana:7.12.1
Kibana连接的是Elasticsearch的REST API端口,而在同一Docker网络中,端口映射并不适用,容器之间直接通过内部端口相互通信(9200端口,指向的是内部9200端口,不是对外暴露的9200端口)
访问:http://服务器id:5601/,出现以下界面表示安装成功
在开发工具中就可以执行DSL操作了
IK分词器
Elasticsearch的关键就是倒排索引,而倒排索引依赖于对文档内容的分词,而分词则需要高效、精准的分词算法,IK分词器就是这样一个中文分词算法。
IK分词器的安装
下载IK分词器
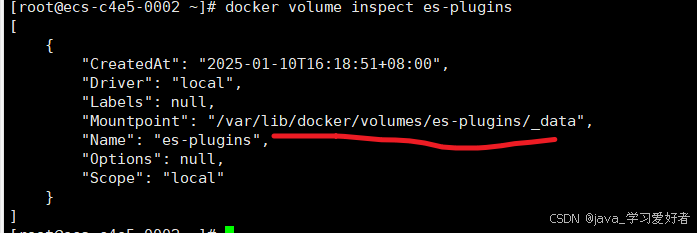
https://release.infinilabs.com/analysis-ik/stable/elasticsearch-analysis-ik-7.12.1.zip查看es-plugins插件容器所在位置
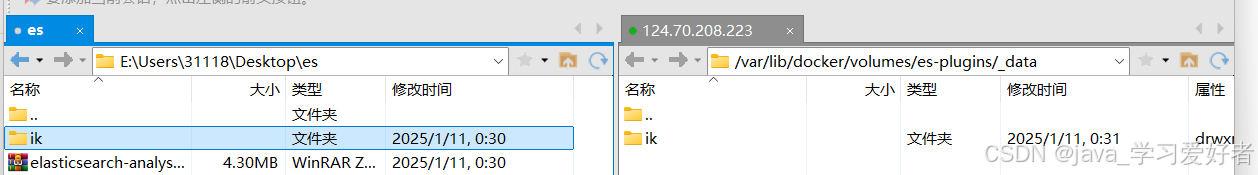
docker volume inspect es-plugins将ik分词器解压后,上传至服务器容器es-plugins所在位置
重启es服务
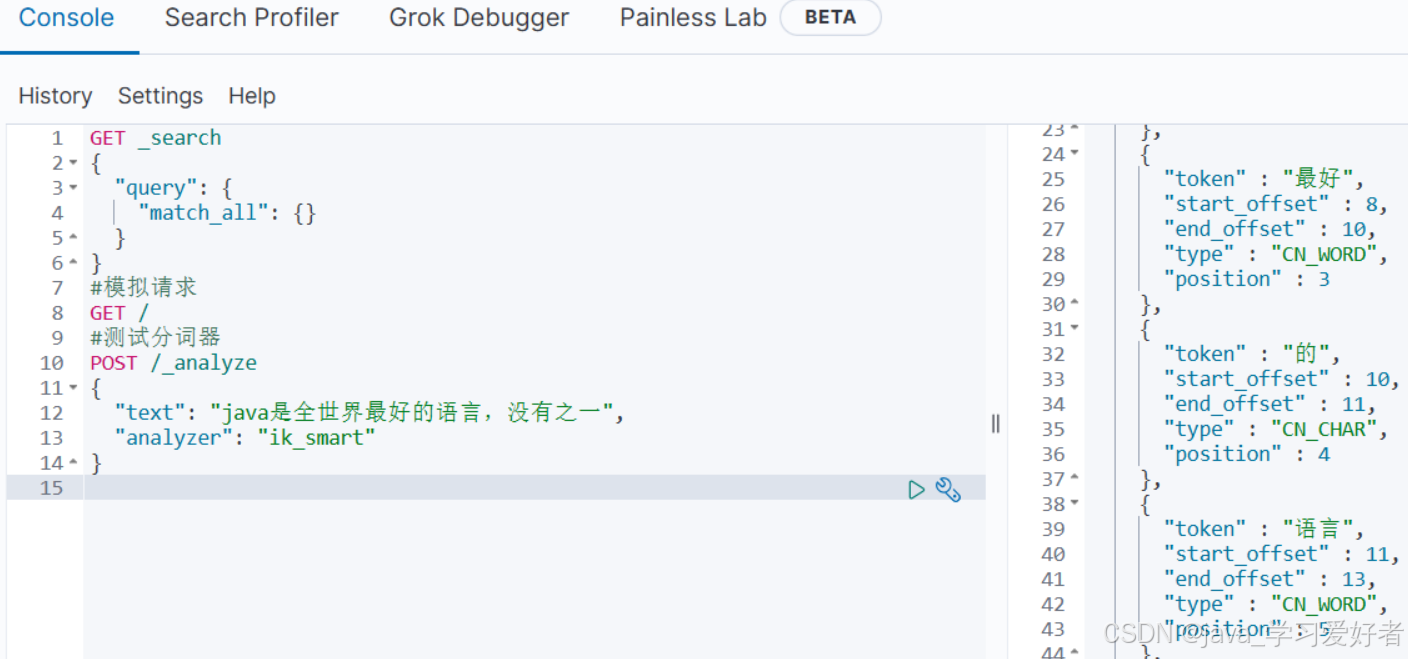
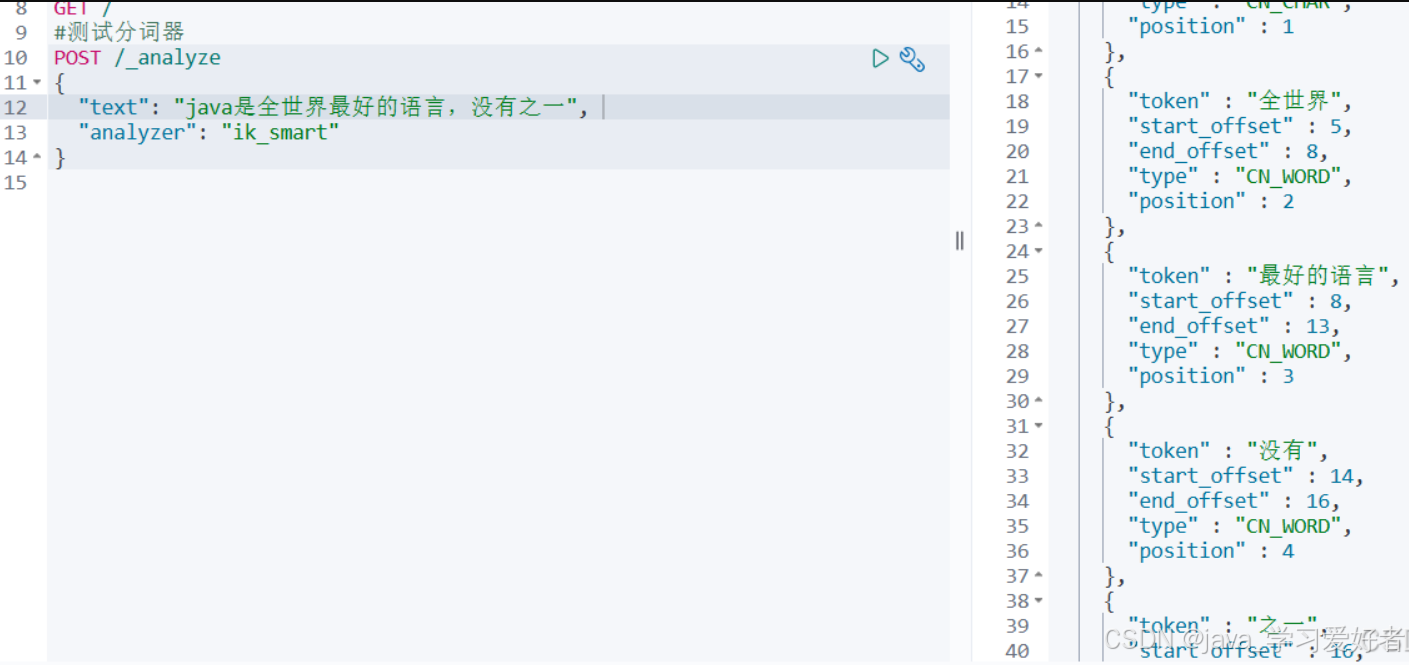
docker restart es进入开发工具界面,对 “java是全世界最好的语言,没有之一”,进行分词
#测试分词器
POST /_analyze
{
"text": "java是全世界最好的语言,没有之一",
"analyzer": "ik_smart"
} ik分词器安装成功
IK分词器的执行模式
IK分词器包含两种模式:
-
ik_smart:智能语义切分 -
ik_max_word:最细粒度切分
扩展词典
打开IK分词器config目录,在IKAnalyzer.cfg.xml配置文件内容添加
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<!DOCTYPE properties SYSTEM "http://java.sun.com/dtd/properties.dtd">
<properties>
<comment>IK Analyzer 扩展配置</comment>
<!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展字典 -->
<entry key="ext_dict"></entry>
<!--用户可以在这里配置自己的扩展停止词字典-->
<entry key="ext_stopwords"></entry>
<!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展字典 -->
<!-- <entry key="remote_ext_dict">words_location</entry> -->
<!--用户可以在这里配置远程扩展停止词字典-->
<!-- <entry key="remote_ext_stopwords">words_location</entry> -->
</properties>
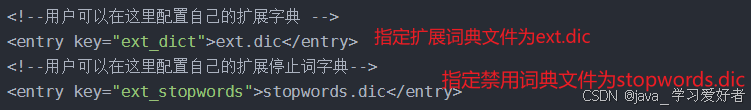
扩展分词"最好的语言"
禁用分词“的”
重启es容器 ,可以看到“最好的语言”已经可以被识别为是一个分词了
索引库操作
-
type:字段数据类型,常见的简单类型有:-
字符串:
text(可分词的文本)、keyword(精确值,例如:品牌、国家、ip地址) -
数值:
long、integer、short、byte、double、float、 -
布尔:
boolean -
日期:
date -
对象:
object
-
-
index:是否创建索引,默认为true -
analyzer:使用哪种分词器 -
properties:该字段的子字段
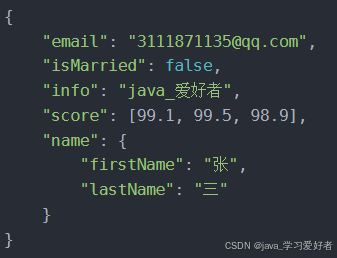
我们以下面这段JSON数据为例,我们为这段数据创建索引库
email:字符串,但是不分词,不创建索引
score:只看数组中元素类型
id:java中id为Lone,而在es中,所有的id默认为字符串
创建索引库
#创建索引库,es中id默认为字符串
PUT /es_test
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id":{
"type":"keyword"
},
"email":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"info":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_smart"
},
"score":{
"type": "float"
},
"name":{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"firstName": {
"type":"keyword"
},
"lastName":{
"type":"keyword"
}
}
}
}
}
}若需要同时根据多个字段搜索,推荐把这些字段复制到统一的一个字段中,分词查询,效率更高
创建一个统一字段all
"all":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word"
}其他需要参与搜索的字段,复制到all中
"copy_to": "all"综上:创建索引方案如下
#创建索引库
PUT /es_test
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"email":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"info":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_smart",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"score":{
"type": "float",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"name":{
"type": "object",
"properties": {
"firstName": {
"type":"keyword"
},
"lastName":{
"type":"keyword"
}
}
},
"all":{
"type":"text",
"analyzer":"ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}
修改索引库
倒排索引结构虽然不复杂,但是一旦数据结构改变(比如改变了分词器),就需要重新创建倒排索引,这简直是灾难。因此索引库一旦创建,无法修改mapping。
虽然无法修改mapping中已有的字段,但是却允许添加新的字段到mapping中,因为不会对倒排索引产生影响。因此修改索引库能做的就是向索引库中添加新字段,或者更新索引库的基础属性。
修改索引库,新增新字段age
PUT /es_test/_mapping
{
"properties": {
"age":{
"type": "integer"
}
}
}查看索引库
GET /es_test删除索引库
DELETE /es_test文档操作
新增文档
新增文档:POST /索引库名/_doc/文档id
POST /es_test/_doc/1
{
"email": "[email protected]",
"info": "java_爱好者",
"age":23,
"score":[98.5,88.3],
"name": {
"firstName": "张",
"lastName": "三"
}
}修改文档
修改有两种方式:
-
全量修改:直接覆盖原来的文档
-
局部修改:修改文档中的部分字段
全量修改
全量修改是覆盖原来的文档,其本质是两步操作:
-
根据指定的id删除文档
-
新增一个相同id的文档
#修改文档-全量修改
PUT /es_test/_doc/1
{
"info": "java是最好的语言",
"email": "....",
"name": {
"firstName": "李",
"lastName": "四"
}
}局部修改
局部修改是只修改指定id匹配的文档中的部分字段
#修改文档-局部修改
POST /es_test/_update/1
{
"doc": {
"email": "[email protected]"
}
}
按id查找文档
#查看文档
GET /es_test/_doc/1批量查找
GET /es_test/_search删除文档
DELETE /es_test/_doc/1RestClient
导入依赖
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
</dependency>覆盖SpringBoot默认的ES版本
<properties>
<elasticsearch.version>7.12.1</elasticsearch.version>
</properties>这里为了单元测试方便,我们创建一个测试类IndexTest,然后将初始化的代码编写在@BeforeEach方法中:
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.springframework.boot.test.context.SpringBootTest;
import java.io.IOException;
@SpringBootTest
class HotelIndexTest {
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://124.70.208.223:9200")
));
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws IOException {
client.close();
}
}
或者直接采用Spring注入
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@Configuration
public class EsConfig {
@Bean
public RestHighLevelClient restHighLevelClient(){
return new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://124.70.208.223:9200")
));
}
}
索引库操作
创建索引库
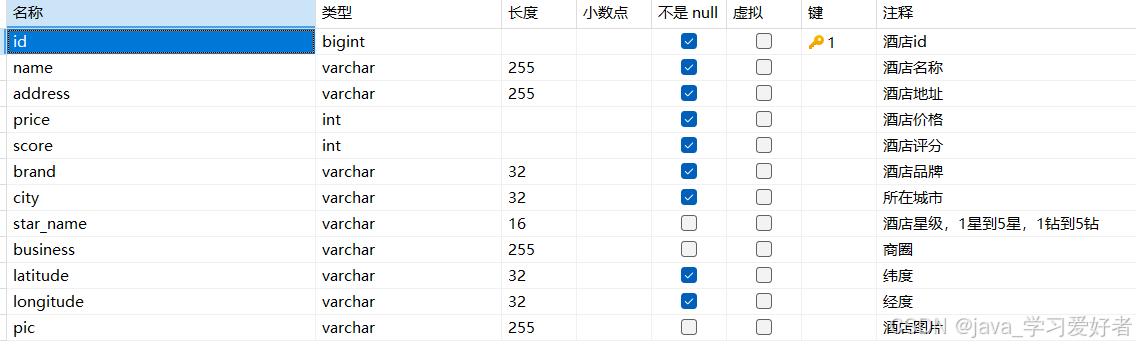
那么我们如何将下列MySQL数据存入es中呢?
创建对应es数据,在es中,经度和纬度作为一个字段存储,以“,”隔开
import lombok.Data;
import lombok.NoArgsConstructor;
@Data
@NoArgsConstructor
public class HotelDoc {
private Long id;
private String name;
private String address;
private Integer price;
private Integer score;
private String brand;
private String city;
private String starName;
private String business;
private String location;
private String pic;
public HotelDoc(Hotel hotel) {
this.id = hotel.getId();
this.name = hotel.getName();
this.address = hotel.getAddress();
this.price = hotel.getPrice();
this.score = hotel.getScore();
this.brand = hotel.getBrand();
this.city = hotel.getCity();
this.starName = hotel.getStarName();
this.business = hotel.getBusiness();
this.location = hotel.getLatitude() + ", " + hotel.getLongitude();
this.pic = hotel.getPic();
}
}
geo_point 是Elasticsearch 中一种专门用于地理点数据的字段类型。它允许你存储和查询地球上的位置信息,通常以纬度和经度的形式表示。
geo_point 类型支持多种地理空间查询,例如距离查询、多边形查询等,并且可以用于聚合操作来分析地理位置数据。
"location":{
"type": "geo_point"
},综上:es中索引库的设置为
PUT /hotel
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"address":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"price":{
"type": "integer"
},
"score":{
"type": "integer"
},
"brand":{
"type": "keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"city":{
"type": "keyword",
"copy_to": "all"
},
"starName":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"business":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"location":{
"type": "geo_point"
},
"pic":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"all":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
}
}
}
}利用RestHighLevelClient 创建索引库
package cn.itcast.hotel.constants;
public class HotelIndexConstants {
public static final String MAPPING_TEMPLATE = "{\n" +
" \"mappings\": {\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"id\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"address\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"index\": false\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"price\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"score\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"brand\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"city\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"starName\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"business\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"copy_to\": \"all\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"pic\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"index\": false\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"location\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"geo_point\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"all\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";
}
@Test
void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request PUT /hotel
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备请求参数
request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON);
// 3.发送请求
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}删除索引库
@Test
void testDeleteIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("hotel");
// 3.发送请求
client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}判断索引库是否存在
@Test
void testExistsIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("hotel");
// 3.发送请求
boolean isExists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
System.out.println(isExists ? "存在" : "不存在");
}文档操作
新增文档
@Test
void testAddDocument() throws IOException {
// 1.查询数据库hotel数据
Hotel hotel = hotelService.getById(61083L);
// 2.转换为HotelDoc
HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel);
// 3.转JSON
String json = JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc);
// 1.准备Request
IndexRequest request = new IndexRequest("hotel").id(hotelDoc.getId().toString());
// 2.准备请求参数DSL,其实就是文档的JSON字符串
request.source(json, XContentType.JSON);
// 3.发送请求
client.index(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}查看指定文档
@Test
void testGetDocumentById() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request // GET /hotel/_doc/{id}
GetRequest request = new GetRequest("hotel", "61083");
// 2.发送请求
GetResponse response = client.get(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 3.解析响应结果
String json = response.getSourceAsString();
HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class);
System.out.println("hotelDoc = " + hotelDoc);
}删除指定文档
@Test
void testDeleteDocumentById() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request // DELETE /hotel/_doc/{id}
DeleteRequest request = new DeleteRequest("hotel", "61083");
// 2.发送请求
client.delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}更新指定文档
@Test
void testUpdateById() throws IOException {
// 1.准备Request
UpdateRequest request = new UpdateRequest("hotel", "61083");
// 2.准备参数
request.doc(
"price", "870"
);
// 3.发送请求
client.update(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}批量添加文档
@Test
void testBulkRequest() throws IOException {
// 查询所有的酒店数据
List<Hotel> list = hotelService.list();
// 1.准备Request
BulkRequest request = new BulkRequest();
// 2.准备参数
for (Hotel hotel : list) {
// 2.1.转为HotelDoc
HotelDoc hotelDoc = new HotelDoc(hotel);
// 2.2.转json
String json = JSON.toJSONString(hotelDoc);
// 2.3.添加请求
request.add(new IndexRequest("hotel").id(hotel.getId().toString()).source(json, XContentType.JSON));
}
// 3.发送请求
client.bulk(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}DSL查询
Elasticsearch的查询可以分为两大类:
-
叶子查询(Leaf query clauses):一般是在特定的字段里查询特定值,属于简单查询,很少单独使用。
-
复合查询(Compound query clauses):以逻辑方式组合多个叶子查询或者更改叶子查询的行为方式。
无条件查询的类型是:match_all,由于match_all无条件,所以条件位置不写即可。因此其查询语句如下
查询所有
查询所有-完整形式
GET /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {
}
}
}查询所有-简写形式
GET /hotel/_search @Test
void testMatchAll() throws IOException {
// 1.准备request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备请求参数
request.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
// 3.发送请求,得到响应
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.结果解析
handleResponse(response);
}
private void handleResponse(SearchResponse response) {
SearchHits searchHits = response.getHits();
// 4.1.总条数
long total = searchHits.getTotalHits().value;
System.out.println("总条数:" + total);
// 4.2.获取文档数组
SearchHit[] hits = searchHits.getHits();
// 4.3.遍历
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
// 4.4.获取source
String json = hit.getSourceAsString();
// 4.5.反序列化,非高亮的
HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class);
// 4.7.打印
System.out.println(hotelDoc);
}
}
虽然是match_all,但是响应结果中并不会包含索引库中的所有文档,而是仅有10条。这是因为处于安全考虑,elasticsearch设置了默认的查询页数。
全文检索查询
GET /{索引库名}/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"字段名": "搜索条件"
}
}
}GET /{索引库名}/_search
{
"query": {
"multi_match": {
"query": "搜索条件",
"fields": ["字段1", "字段2"]
}
}
} @Test
void testMatch() throws IOException {
// 1.准备request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备请求参数
// request.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all", "外滩如家"));
request.source().query(QueryBuilders.multiMatchQuery("外滩如家", "name", "brand", "city"));
// 3.发送请求,得到响应
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.结果解析
handleResponse(response);
}精确查询
range是范围查询,对于范围筛选的关键字有:
-
gte:大于等于 -
gt:大于 -
lte:小于等于 -
lt:小于
GET /{索引库名}/_search
{
"query": {
"range": {
"字段名": {
"gte": {最小值},
"lte": {最大值}
}
}
}
} @Test
void testBool() throws IOException {
// 1.准备request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备请求参数
/*
BoolQueryBuilder boolQuery = QueryBuilders.boolQuery();
// 2.1.must
boolQuery.must(QueryBuilders.termQuery("city", "杭州"));
// 2.2.filter
boolQuery.filter(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price").lte(250));
*/
request.source().query(
QueryBuilders.boolQuery()
.must(QueryBuilders.termQuery("city", "杭州"))
.filter(QueryBuilders.rangeQuery("price").lte(250))
);
// 3.发送请求,得到响应
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.结果解析
handleResponse(response);
}地理查询
查询该地点附近5公里内的所以酒店
GET /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"geo_distance":{
"distance":"4km",
"location":"31.25,121.47"
}
}
}
@Test
void testDistance() throws IOException {
// 1.准备request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
GeoDistanceQueryBuilder geoDistanceQuery = QueryBuilders.geoDistanceQuery("location")
.point(31.25, 121.47) // 纬度, 经度
.distance("4km");
request.source().query(geoDistanceQuery);
// 3.发送请求,得到响应
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.结果解析
handleResponse(response);
}算分函数查询
当我们利用match查询时,文档结果会根据与搜索词条的关联度打分(_score),返回结果时按照分值降序排列。
从elasticsearch5.1开始,采用的相关性打分算法是BM25算法,公式如下:
基于这套公式,就可以判断出某个文档与用户搜索的关键字之间的关联度,还是比较准确的。但是,在实际业务需求中,常常会有竞价排名的功能。不是相关度越高排名越靠前,而是掏的钱多的排名靠前。
function score 查询中包含四部分内容:
原始查询条件:query部分,基于这个条件搜索文档,并且基于BM25算法给文档打分,原始算分(query score)
过滤条件:filter部分,符合该条件的文档才会重新算分
算分函数:符合filter条件的文档要根据这个函数做运算,得到的函数算分(function score),有四种函数
weight:函数结果是常量
field_value_factor:以文档中的某个字段值作为函数结果
random_score:以随机数作为函数结果
script_score:自定义算分函数算法
运算模式:算分函数的结果、原始查询的相关性算分,两者之间的运算方式,包括:
multiply:相乘
replace:用function score替换query score
其它,例如:sum、avg、max、min
GET /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"function_score": {
"query": { .... }, // 原始查询,可以是任意条件
"functions": [ // 算分函数
{
"filter": { // 满足的条件,品牌必须是Iphone
"term": {
"brand": "Iphone"
}
},
"weight": 10 // 算分权重为2
}
],
"boost_mode": "multipy" // 加权模式,求乘积
}
}
}- 文档 A 的原始得分为
x,因为它的品牌是"Iphone",所以它的最终得分将是x * 10。 - 文档 B 的原始得分为
y,因为它不符合filter条件,所以它的最终得分仍然是y,不会受到weight的影响。
bool查询
bool查询,即布尔查询。就是利用逻辑运算来组合一个或多个查询子句的组合。bool查询支持的逻辑运算有:
must:必须匹配每个子查询,类似“与”
should:选择性匹配子查询,类似“或”
must_not:必须不匹配,不参与算分,类似“非”
filter:必须匹配,不参与算分
GET /items/_search
{
"query": {
"bool": {
"must": [
{"match": {"name": "手机"}}
],
"should": [
{"term": {"brand": { "value": "vivo" }}},
{"term": {"brand": { "value": "小米" }}}
],
"must_not": [
{"range": {"price": {"gte": 2500}}}
],
"filter": [
{"range": {"price": {"lte": 1000}}}
]
}
}
}出于性能考虑,与搜索关键字无关的查询尽量采用must_not或filter逻辑运算,避免参与相关性算分。
分页排序
elasticsearch默认是根据相关度算分(_score)来排序,但是也支持自定义方式对搜索结果排序。不过分词字段无法排序,能参与排序字段类型有:keyword类型、数值类型、地理坐标类型、日期类型等
elasticsearch 默认情况下只返回top10的数据。而如果要查询更多数据就需要修改分页参数了。
基础分页
elasticsearch中通过修改
from、size参数来控制要返回的分页结果:
from:从第几个文档开始
size:总共查询几个文档
类似于mysql中的limit ?, ?
GET /items/_search
{
"query": {
"match_all": {}
},
"from": 0, // 分页开始的位置,默认为0
"size": 10, // 每页文档数量,默认10
"sort": [
{
"price": {
"order": "desc"
}
}
]
}
@Test
void testSortAndPage() throws IOException {
int page = 2,size = 5;
// 1.准备request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备请求参数
// 2.1.query
request.source()
.query(QueryBuilders.matchAllQuery());
// 2.2.排序sort
request.source().sort("price", SortOrder.ASC);
// 2.3.分页 from\size
request.source().from((page - 1) * size).size(size);
// 3.发送请求,得到响应
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.结果解析
handleResponse(response);
}
高亮
什么是高亮显示呢?
我们在百度,京东搜索时,关键字会变成红色,比较醒目,这叫高亮显示
观察页面源码,你会发现两件事情:
高亮词条都被加了
<em>标签
<em>标签都添加了红色样式
css样式肯定是前端实现页面的时候写好的,但是前端编写页面的时候是不知道页面要展示什么数据的,不可能给数据加标签。而服务端实现搜索功能,要是有elasticsearch做分词搜索,是知道哪些词条需要高亮的。
因此词条的高亮标签肯定是由服务端提供数据的时候已经加上的。
因此实现高亮的思路就是:
用户输入搜索关键字搜索数据
服务端根据搜索关键字到elasticsearch搜索,并给搜索结果中的关键字词条添加
html标签前端提前给约定好的
html标签添加CSS样式
事实上elasticsearch已经提供了给搜索关键字加标签的语法,无需我们自己编码。
GET /{索引库名}/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"搜索字段": "搜索关键字"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"高亮字段名称": {
"pre_tags": "<em>",
"post_tags": "</em>"
}
}
}
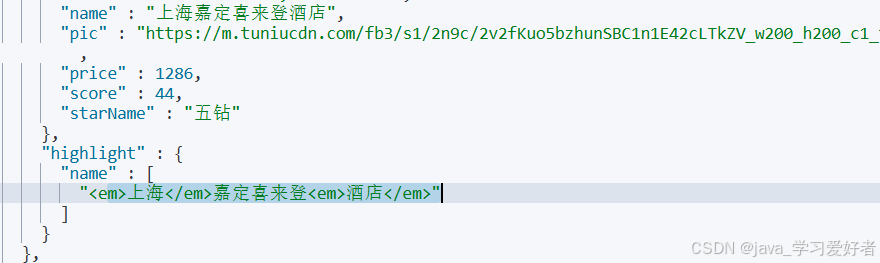
}GET /hotel/_search
{
"query": {
"match": {
"name": "酒店上海"
}
},
"highlight": {
"fields": {
"name": {
"pre_tags": "<em>",
"post_tags": "</em>"
}
}
}
} @Test
void testHighlight() throws IOException {
// 1.准备request
SearchRequest request = new SearchRequest("hotel");
// 2.准备请求参数
// 2.1.query
request.source().query(QueryBuilders.matchQuery("all", "外滩如家"));
// 2.2.高亮
request.source().highlighter(new HighlightBuilder().field("name").requireFieldMatch(false));
// 3.发送请求,得到响应
SearchResponse response = client.search(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 4.结果解析
handleResponse(response);
}
private void handleResponse(SearchResponse response) {
SearchHits searchHits = response.getHits();
// 4.1.总条数
long total = searchHits.getTotalHits().value;
System.out.println("总条数:" + total);
// 4.2.获取文档数组
SearchHit[] hits = searchHits.getHits();
// 4.3.遍历
for (SearchHit hit : hits) {
// 4.4.获取source
String json = hit.getSourceAsString();
// 4.5.反序列化,非高亮的
HotelDoc hotelDoc = JSON.parseObject(json, HotelDoc.class);
// 4.6.处理高亮结果
// 1)获取高亮map
Map<String, HighlightField> map = hit.getHighlightFields();
// 2)根据字段名,获取高亮结果
HighlightField highlightField = map.get("name");
// 3)获取高亮结果字符串数组中的第1个元素
String hName = highlightField.getFragments()[0].toString();
// 4)把高亮结果放到HotelDoc中
hotelDoc.setName(hName);
// 4.7.打印
System.out.println(hotelDoc);
}
}