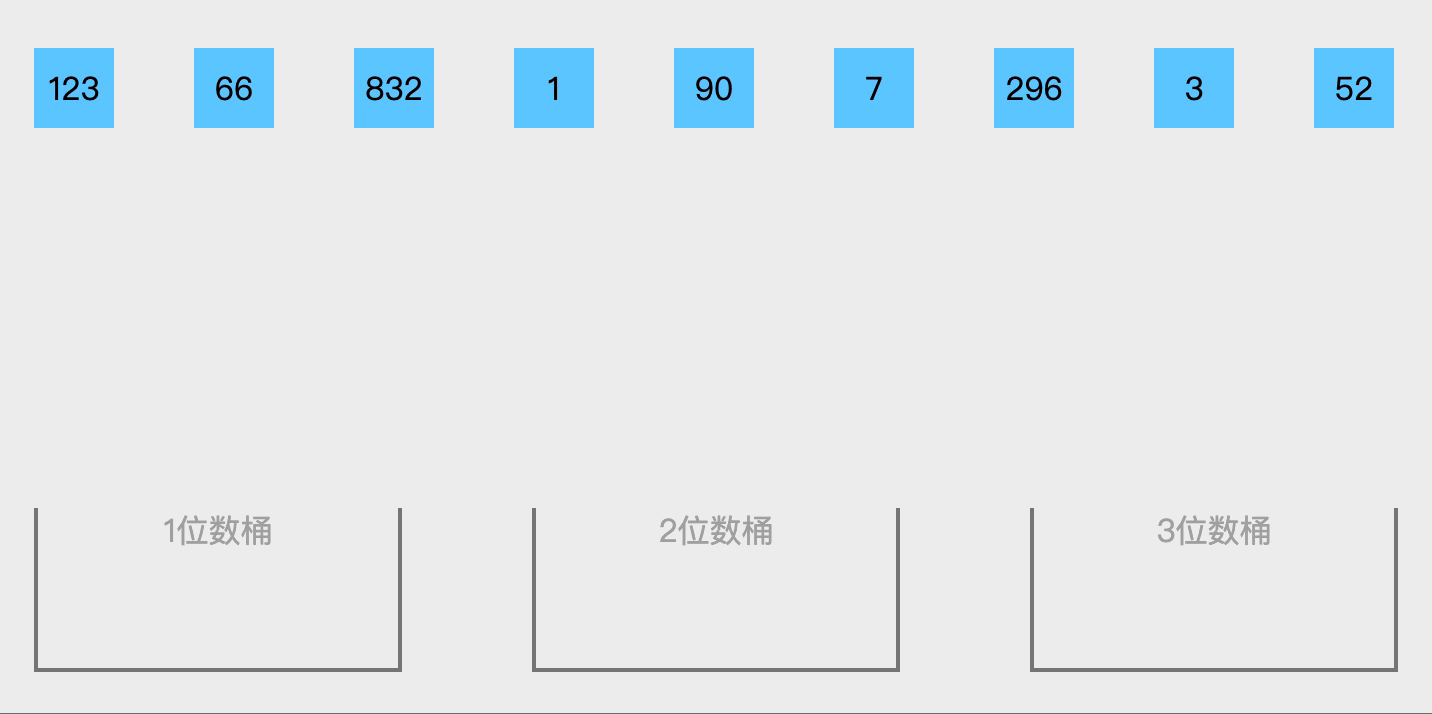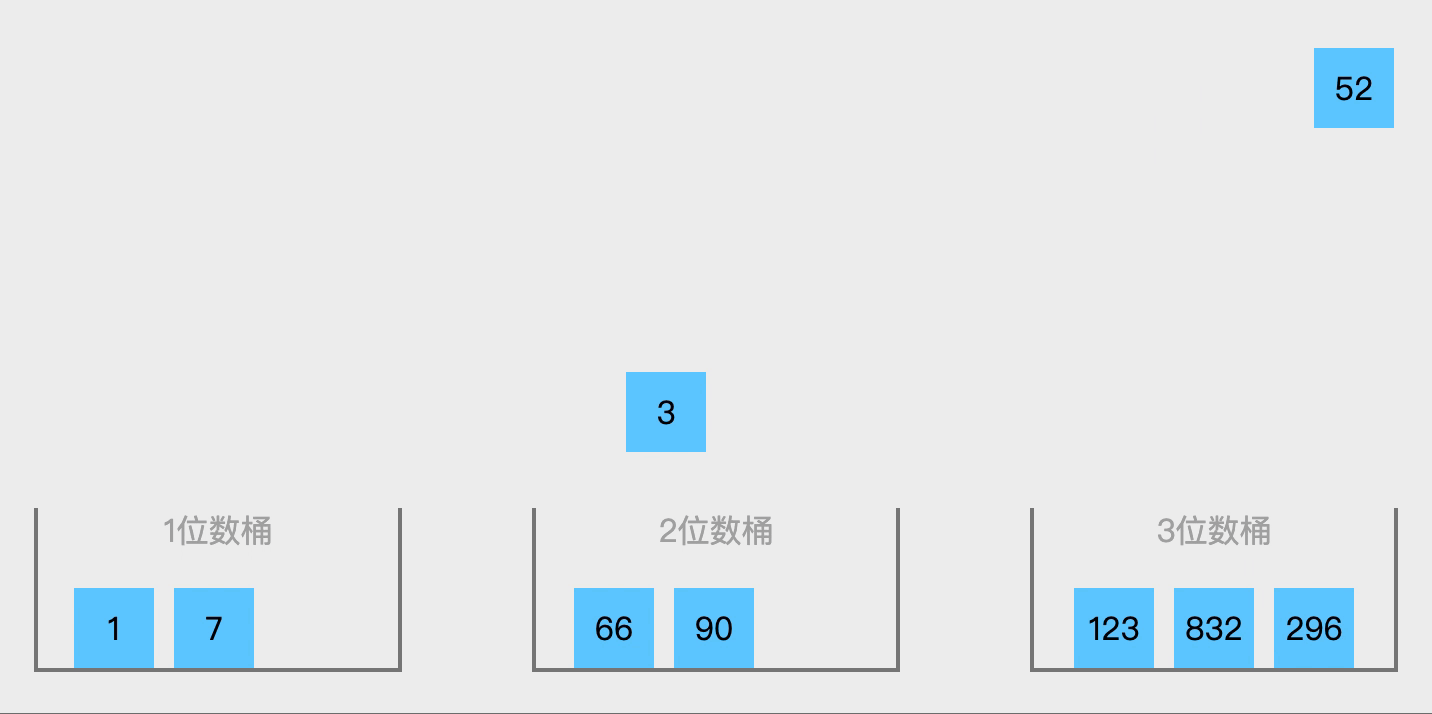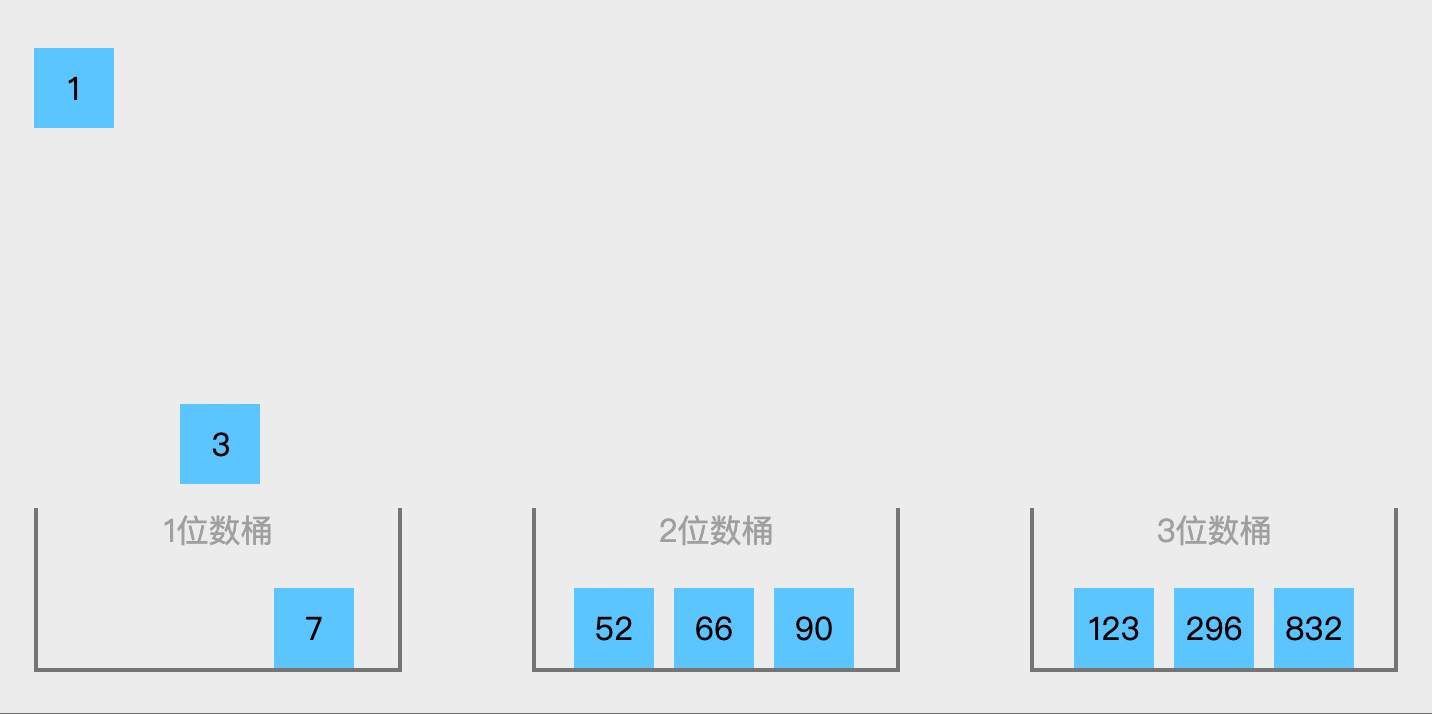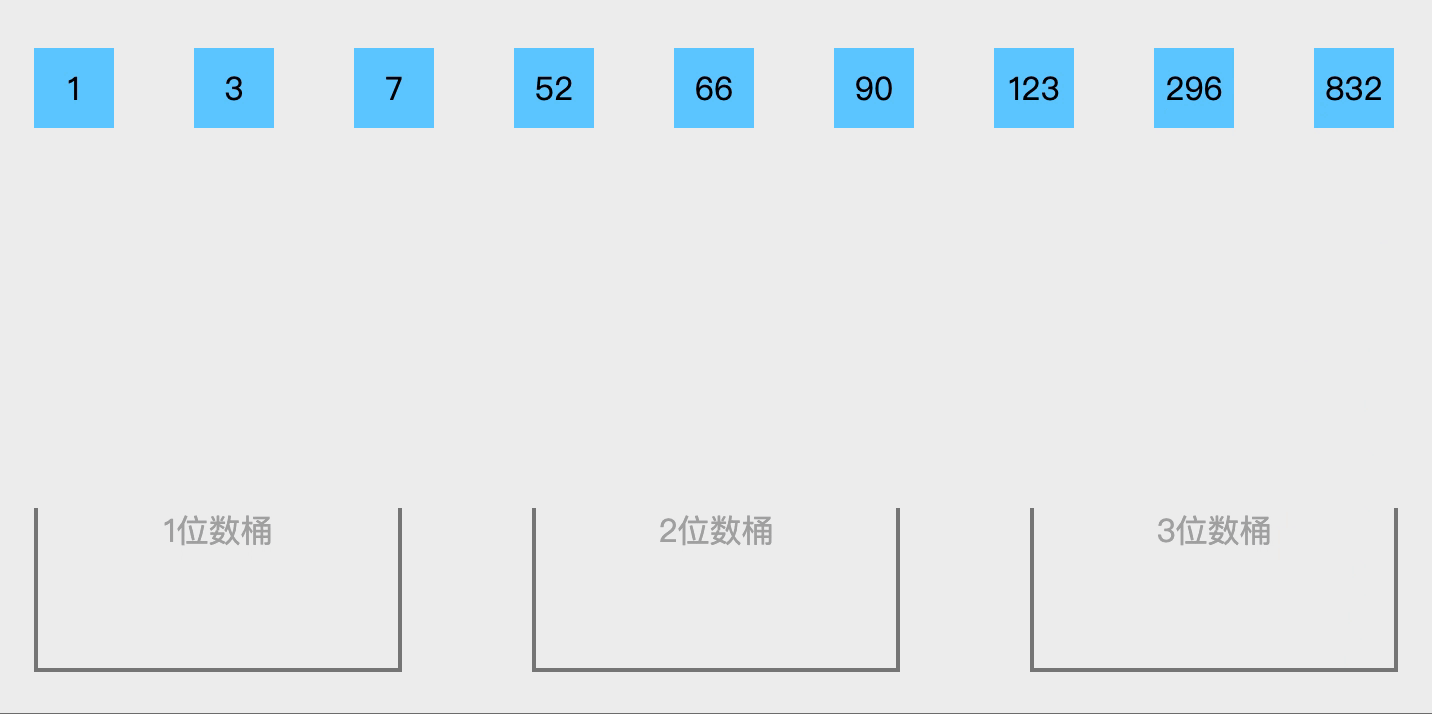
核心思想为分区间排序后合并。适用于数据均匀分布在一个范围内,或浮点数排序或范围明确的数据。如果需要处理整数或其他数据范围,可以通过调整BUCKET_RANGE的计算方式实现,例如对[0,100)的整数排序:
int index = arr[i] / 10; // 每10个单位一个桶
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
// 桶结构体(动态数组实现)
typedef struct {
float* data; // 桶内数据
int count; // 当前元素数量
int capacity; // 桶容量
} Bucket;
// 创建桶并初始化
Bucket create_bucket(int init_capacity) {
Bucket b;
b.data = (float*)malloc(init_capacity * sizeof(float));
assert(b.data != NULL);
b.count = 0;
b.capacity = init_capacity;
return b;
}
// 向桶中插入元素(自动扩容)
void bucket_insert(Bucket* b, float value) {
if (b->count >= b->capacity) {
b->capacity *= 2;
b->data = (float*)realloc(b->data, b->capacity * sizeof(float));
assert(b->data != NULL);
}
b->data[b->count++] = value;
}
// 释放桶内存
void free_bucket(Bucket* b) {
free(b->data);
b->count = b->capacity = 0;
}
// 插入排序(用于桶内排序)
void insertion_sort(float arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
float key = arr[i];
int j = i - 1;
while (j >= 0 && arr[j] > key) {
arr[j + 1] = arr[j];
j--;
}
arr[j + 1] = key;
}
}
// 桶排序主函数
void bucket_sort(float arr[], int n) {
const int BUCKET_NUM = 10; // 桶数量
const float BUCKET_RANGE = 0.1f; // 每个桶的范围跨度(示例为[0,1)区间)
// 1. 初始化桶数组
Bucket* buckets = (Bucket*)malloc(BUCKET_NUM * sizeof(Bucket));
assert(buckets != NULL);
for (int i = 0; i < BUCKET_NUM; i++) {
buckets[i] = create_bucket(4); // 初始容量为4
}
// 2. 将元素分配到桶中
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
// 计算桶索引(适用于[0,1)区间的浮点数)
int index = (int)(arr[i] / BUCKET_RANGE);
bucket_insert(&buckets[index], arr[i]);
}
// 3. 对每个桶进行排序并合并
int arr_index = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < BUCKET_NUM; i++) {
if (buckets[i].count > 0) {
// 使用插入排序对桶内元素排序
insertion_sort(buckets[i].data, buckets[i].count);
// 将排序后的桶元素复制回原数组
for (int j = 0; j < buckets[i].count; j++) {
arr[arr_index++] = buckets[i].data[j];
}
}
free_bucket(&buckets[i]); // 释放桶内存
}
free(buckets); // 释放桶数组
}
#include <stdio.h>
// 打印浮点数组(保留两位小数)
void print_float_array(float arr[], int n) {
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
printf("%.2f ", arr[i]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
// 测试数据(0~1之间的浮点数)
float arr[] = {0.78, 0.17, 0.39, 0.26, 0.72, 0.94, 0.21, 0.12, 0.23, 0.68};
int n = sizeof(arr) / sizeof(arr[0]);
printf("排序前: ");
print_float_array(arr, n);
bucket_sort(arr, n);
printf("排序后: ");
print_float_array(arr, n);
return 0;
}优化建议
1.动态扩容机制,减少内存碎片化
2.小桶使用插入排序,对局部数据高效
3.根据数据分布预估桶大小,内存预分配