一、二叉堆与优先队列
优先队列Priority Queue
- 默认的队列是FIFO,队列有一种变体称为优先队列
- 优先队列的出队:跟默认队列一样从队首出队
- 优先队列的入队:数据项的次序由优先级来确定,高优先级的数据项排在前面,反之排在后面
优先队列的实现-二叉堆Binary Heap
- 实现优先队列的经典方案是采用二叉堆数据结构,二叉堆能够将优先队列的入队和出队复杂度都保持在
O(log n) - 最小key排在队首的称为**“最小堆minheap”**(下面以最小堆为例)。反之,最大key排在队首的是“最大堆max heap”
- 堆次序Heap Order:任何一个节点x,其父节点p中的key均小于x中的key。这样的二叉树符合“堆”性质,其中任何一条路径,均是一个已排序数列。此时根节点的key最小。
抽象数据类型-二叉堆
| 方法签名 | 描述 |
|---|---|
| BinaryHeap() | 创建一个空二叉堆对象 |
| insert(k) | 将新key加入到堆中 |
| findMin() | 返回堆中的最小项,最小项仍保留在堆中 |
| delMin() | 返回堆中的最小项,同时从堆中删除 |
| isEmpty() | 返回堆是否为空 |
| size() | 返回堆中key的个数 |
| buildHeap(list) | 从一个key列表创建新堆 |
二叉堆的实现-非嵌套列表
- 为了使堆操作能保持在对数水平上,需要采用二叉树结构。同时,需要保持二叉树的“平衡”,因此采用完全二叉树结构来近似实现“平衡。
- 完全二叉树:叶节点最多只出现在最底层和次底层,而且最底层的叶节点都连续集中在最左边,每个内部节点都有两个子节点,最多可有1个节点例外
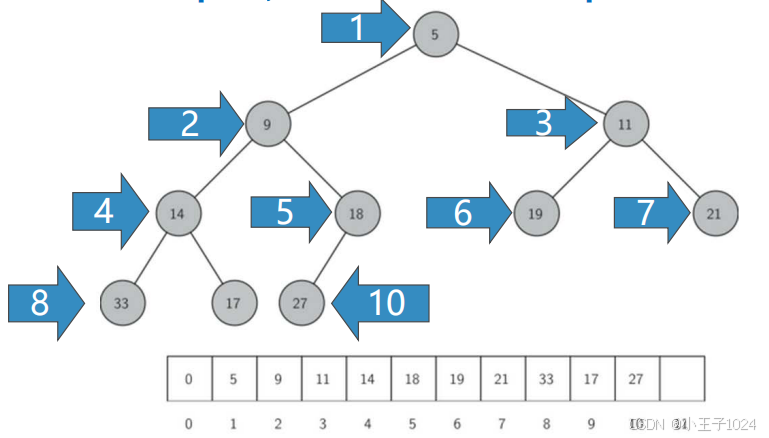
- 完全二叉树由于其特殊性,可以用非嵌套列表实现。如果节点的下标为p,那么其左子节点下标为2p,右子节点为2p+1,其父节点下标为p//2
二、二叉堆的实现
二叉堆的实现
- 二叉堆初始化:使用非嵌套列表,其中表首下标为0的项用数字0点位
- insert方法:为了保持“完全二叉树”的性质,新key加在列表末尾,然后将新key沿着路径来**“上浮”**到其正确位置,直到比父节点大,从而保持堆次序。
- delMin方法:为了保持“完全二叉树”的性质,用最后一个节点来代替根节点;然后将新的根节点沿着一条路径“下沉”,直到比两个子节点都小,从而保持堆次序。
用Python实现抽象数据类型-二叉堆
class BinaryHeap:
def __init__(self):
self.heap_list = [0]
self.count = 0
def perc_up(self, i):
"""数据项上浮"""
while i // 2 > 0:
# 如果当前节点小于其父节点,则进行交换
if self.heap_list[i] < self.heap_list[i // 2]:
self.heap_list[i], self.heap_list[i // 2] = (
self.heap_list[i // 2],
self.heap_list[i],
)
i = i // 2
else:
break
def insert(self, key):
# 新key加在列表末尾
self.heap_list.append(key)
self.count += 1
# 新key进行上浮
self.perc_up(self.count)
def find_min(self):
return self.heap_list[1] if self.count > 0 else None
def perc_down(self, i):
"""数据项下沉"""
while 2 * i <= self.count:
# 找出左右子节点中,较小的一位
if (
2 * i + 1 <= self.count
and self.heap_list[2 * i + 1] < self.heap_list[2 * i]
):
min_child_idx = 2 * i + 1
else:
min_child_idx = 2 * i
# 如果当前节点大于其子节点,则进行交换
if self.heap_list[i] > self.heap_list[min_child_idx]:
self.heap_list[min_child_idx], self.heap_list[i] = (
self.heap_list[i],
self.heap_list[min_child_idx],
)
i = min_child_idx
else:
break
def del_min(self):
if self.count == 0:
return None
if self.count == 1:
self.count = 0
return self.heap_list.pop()
min_val = self.heap_list[1]
# 最后一个数据项出列,其值放到第1位
key = self.heap_list.pop()
self.heap_list[1] = key
self.count -= 1
# 进行下沉操作
self.perc_down(1)
return min_val
def is_empty(self):
return self.count == 0
def size(self):
return self.count
def build_heap(self, lst1):
"""从一个key列表创建新堆"""
self.heap_list = [0] + lst1[:]
self.count = len(lst1)
# 从最后节点的父节点开始进行下沉
i = self.count // 2
while i > 0:
self.perc_down(i)
i -= 1
def is_heap_order(self):
"""检查当前状态是否符合堆次序"""
for i in range(2, self.count + 1):
if self.heap_list[i // 2] > self.heap_list[i]:
return False
return True
三、二叉堆的应用-堆排序
一个无序表,如何生成二叉堆:
- 方法一:使用逐个insert方法
test_lst = [33, 18, 27, 11, 9, 17, 14, 5, 19, 21]
bh = BinaryHeap()
for i in test_lst:
bh.insert(i)
print(f"二叉堆当前状态:{bh.heap_list}", bh.is_heap_order())
### 输出结果
二叉堆当前状态:[0, 5, 9, 14, 11, 18, 27, 17, 33, 19, 21] True
- 方法二:使用非叶子节点**“下沉”**方法
test_lst = [33, 18, 27, 11, 9, 17, 14, 5, 19, 21]
bh = BinaryHeap()
bh.build_heap(test_lst)
print(f"二叉堆当前状态:{bh.heap_list}", bh.is_heap_order())
### 输出结果
二叉堆当前状态:[0, 5, 9, 14, 11, 21, 17, 27, 18, 19, 33] True
二叉堆的应用-堆排序
- 先将无序表生成二叉堆,然后依次返回堆中的最小项
from my_heap import BinaryHeap
def heap_sort(lst):
bh = BinaryHeap()
bh.build_heap(lst)
return [bh.del_min() for _ in range(bh.size())]
test_list = [18, 48, 85, 67, 44, 36, 53, 32, 3, 5]
print(heap_sort(test_list))
### 输出结果
[3, 5, 18, 32, 36, 44, 48, 53, 67, 85]
您正在阅读的是《数据结构与算法Python版》专栏!关注不迷路~