C++中vector和set都是非常方便的容器,
sort方法是algorithm头文件里的一个标准函数,能进行高效的排序,默认是按元素从小到大排序
将sort方法用到vector和set中能实现多种符合自己需求的排序
首先sort方法可以对静态的数组进行排序
1 #include<iostream>
2 using namespace std;
3 int main(){
4 int a[10] = { 9, 0, 1, 2, 3, 7, 4, 5, 100, 10 };
5 sort(a, a +10);
6 for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
7 cout << a[i] << endl;
8 return 0;
9 }
运行结果:
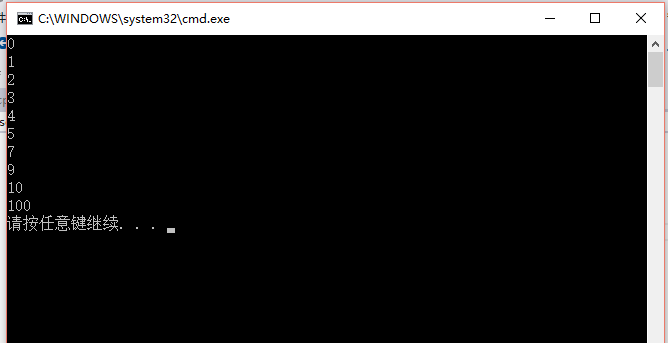
这里可以看到是sort(a,a+10),但是数组a一共只有9个元素,为什么是a+10而不是a+9呢?
因为sort方法实际上最后一位地址对应的数是不取的,
而且vector,set,map这些容器的end()取出来的值实际上并不是最后一个值,而end的前一个才是最后一个值!
需要用prev(xxx.end()),才能取出容器中最后一个元素。
对vector使用sort函数:
第一种情形:基本类型,如vector<int>,vector<double>,vector<string>也是可以的
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<vector>
3 #include<algorithm>
4 using namespace std;
5 int main(){
6 vector<int> a;
7 int n = 5;
8 while (n--){
9 int score;
10 cin >> score;
11 a.push_back(score);
12 }
13 //cout <<" a.end()"<< *a.end() << endl; 执行这句话会报错!
14 cout << " prev(a.end)" << *prev(a.end()) << endl;
15 sort(a.begin(), a.end());
16 for (vector<int>::iterator it = a.begin(); it != a.end(); it++){
17 cout << *it << endl;
18 }
19 return 0;
20 }
执行结果:
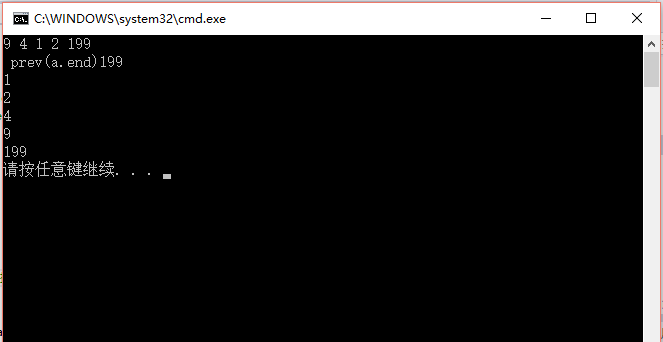
看到了吗,实际上end的前一个指针指向的元素才是插入时的最后一个值!
排序后从小大大。
第二种情形:用自定义的结构体进行sort算法,
这时候需要自己定义个比较函数,因为sort算法是基于容器中的元素是可以两两比较的,然后从小到大排序,所以要自定义怎么样才是小于('<')
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<vector>
3 #include<set>
4 #include<string>
5 #include<algorithm>
6 using namespace std;
7 struct student{
8 char name[10];
9 int score;
10 };
11 //自定义“小于”
12 bool comp(const student &a, const student &b){
13 return a.score < b.score;
14 }
15 int main(){
16 vector<student> vectorStudents;
17 int n = 5;
18 while (n--){
19 student oneStudent;
20 string name;
21 int score;
22 cin >> name >> score;
23 strcpy(oneStudent.name, name.c_str());
24 oneStudent.score = score;
25 vectorStudents.push_back(oneStudent);
26 }
27 cout << "===========排序前================" << endl;
28 for (vector<student>::iterator it = vectorStudents.begin(); it != vectorStudents.end(); it++){
29 cout << "name: " << it->name << " score: " << it->score << endl;
30 }
31 sort(vectorStudents.begin(),vectorStudents.end(),comp);
32 cout << "===========排序后================" << endl;
33 for (vector<student>::iterator it = vectorStudents.begin(); it != vectorStudents.end(); it++){
34 cout << "name: " << it->name << " score: " << it->score << endl;
35 }
36 return 0;
37 }
运行结果:
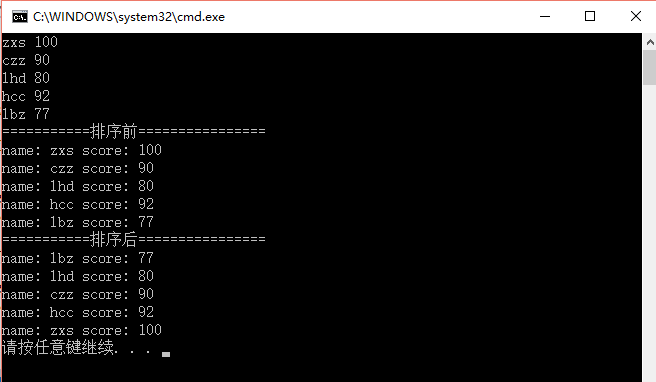
不过有时候一个排序条件不够,比如要求学生按分数从高到低排序,如果分数相同,则按照年龄从大到小排序
就需要在comp自定义函数里面修改一下判断了,原来是直接return a.score < b.score
现在就需要判断
if (a.score > b.score)
return true;
else if (a.score == b.score && a.age > b.age)
return true;
else
return false;这里一定要记得else return false!!!有一次比赛的时候写到这个函数,有三个判断条件,结果忘了这茬,总是报错,到后来有点着急了就自己手动实现了一下写了三个比较函数,调用了三次sort函数!!!!!
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<vector>
3 #include<set>
4 #include<string>
5 #include<algorithm>
6 using namespace std;
7 struct student{
8 char name[10];
9 int score;
10 int age;
11 };
12 //自定义“小于”
13 bool comp(const student &a, const student &b){
14 if (a.score > b.score)
15 return true;
16 else if (a.score == b.score && a.age > b.age)
17 return true;
18 else ///这里的else return false非常重要!!!!!
19 return false;
20 }
21 int main(){
22 vector<student> vectorStudents;
23 /*set<student> setStudents;*/
24 //int n = 5;
25 int n = 6;
26 while (n--){
27 student oneStudent;
28 string name;
29 int score;
30 int age;
31 cin >> name >> score>>age;
32 strcpy(oneStudent.name, name.c_str());
33 oneStudent.score = score;
34 oneStudent.age = age;
35 vectorStudents.push_back(oneStudent);
36 }
37 cout << "===========排序前================" << endl;
38 for (vector<student>::iterator it = vectorStudents.begin(); it != vectorStudents.end(); it++){
39 cout << "name: " << it->name << " score: " << it->score << " age: "<<it->age<<endl;
40 }
41 sort(vectorStudents.begin(), vectorStudents.end(), comp);
42 //sort(setStudents.begin(), setStudents.end());
43 cout << "===========排序后================" << endl;
44 for (vector<student>::iterator it = vectorStudents.begin(); it != vectorStudents.end(); it++){
45 cout << "name: " << it->name << " score: " << it->score << " age: " << it->age << endl;
46 }
47 return 0;
48 }
运行结果如下:
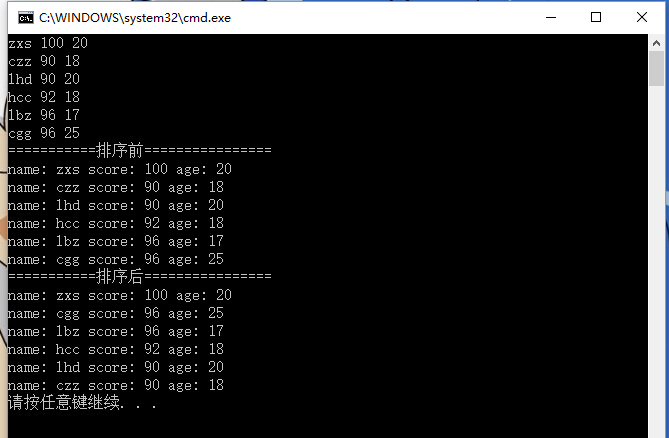
接下来,对于set做类似的操作。
set是一个集合,内部的元素不会重复,同时它会自动进行排序,也是从小到大
而且set的insert方法没有insert(a,cmp)这种重载,所以如果要把结构体插入set中,我们就要重载'<'运算符。
set方法在插入的时候也是从小到大的,那么我们重载一下<运算符让它从大到小排序
1 #include<iostream>
2 #include<vector>
3 #include<set>
4 #include<string>
5 #include<algorithm>
6 using namespace std;
7 struct student{
8 char name[10];
9 int score;
10 };
11 //自定义“小于”
12 bool comp(const student &a, const student &b){
13 return a.score < b.score;
14 }
15 bool operator < (const student & stu1,const student &stu2){
16 return stu1.score > stu2.score;
17 }
18 int main(){
19 //vector<student> vectorStudents;
20 set<student> setStudents;
21 //int n = 5;
22 int n = 6;
23 while (n--){
24 student oneStudent;
25 string name;
26 int score;
27 cin >> name >> score;
28 strcpy(oneStudent.name, name.c_str());
29 oneStudent.score = score;
30 setStudents.insert(oneStudent);
31 }
32 cout << "===========排序前================" << endl;
33 for (set<student>::iterator it = setStudents.begin(); it != setStudents.end(); it++){
34 cout << "name: " << it->name << " score: " << it->score << endl;
35 }
36 //sort(setStudents.begin(), setStudents.end(), comp);
37 //cout << "===========排序后================" << endl;
38 //for (set<student>::iterator it = setStudents.begin(); it != setStudents.end(); it++){
39 // cout << "name: " << it->name << " score: " << it->score << endl;
40 //}
41 return 0;
42 }
运行结果:
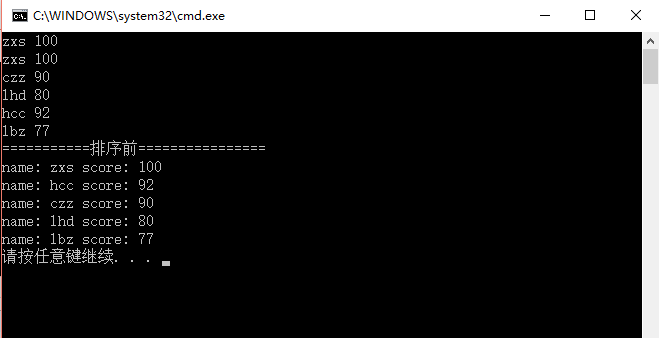
我们可以看到,set内元素不会重复,而且它按照它所认为的“从小到大”进行了排序